Liquid solutions are obtained when the solvent is liquid. The solute can be a gas, liquid or a solid. In this section we will discuss the liquid solutions containing solid or liquid solutes. In such solutions the solute may or may not be volatile. We shall limit our discussion to the binary solution of the solid in liquid and liquid in liquid. Before we discuss the properties of these solution let us study about the vapour pressure of liquid.
When a liquid is taken in a beaker covered from above at certain temperature, a part of the liquid evaporates and its vapours fill the space available to them. The vapours formed will have an inclination to change back to its liquid state by the procedure of condensation. Gradually, equilibrium will be established between liquid and vapour phases. The pressure exerted by the vapours above the liquid surface in equilibrium with the liquid surface in equilibrium with the liquid at a given temperature is called vapour pressure of the liquid.
The vapour pressure of a liquid depends on Nature of liquid
Liquid which have weak intermolecular forces, are volatile and have greater vapour pressure. For instance, dimethyl ether has higher vapour pressure than ethyl alcohol.
Temperature
Vapour pressure increases with the increase in temperature. This is due to the increase in temperature through which more molecules of the liquid can go into vapour phase.
The variation of vapour pressure of a liquid with temperature is given by the Claussius Clapeyron's equation.
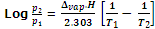 where, p1 and p2 are vapour pressures at temperature T1 and T2 respectively. Δvap.H is enthalpy of vaporization of liquid and R is universal gas constant.
where, p1 and p2 are vapour pressures at temperature T1 and T2 respectively. Δvap.H is enthalpy of vaporization of liquid and R is universal gas constant.
Vapour pressure of the solution of solids in liquids
Let us consider the addition of a small amount of non-volatile solute such as glucose, sucrose, sodium chloride etc. to the liquid (solvent such as water) to form a solution. In such a case the vapour pressure of the solution is solely due to the solvent, as the solute is non-volatile. It is found that the vapour pressure of the solution is lower than that of the pure solvent.
Explanation: the lowering of vapour pressure can be explained on the basis of the surface area of the liquid from which evaporation occurs. In the case of the solution, a part of the liquid surface is occupied by solute particles, which are non-volatile. Therefore, evaporation of the liquid will take place from a lesser surface area. In other words, the particles (or molecules) of the liquid will now have a less tendency to escape into vapour state. This shall, therefore, result in lowering of vapour pressure.