When the forces of attraction existing between adsorbate and adsorbent are van der Waal's forces, the adsorption is called physical adsorption. This type of adsorption is also known as physisorption or van der Waal's adsorption. Since the forces existing between adsorbent and adsorbate are very weak, therefore, this type of adsorption can be easily reversed by heating or by decreasing the pressure.
Characteristics of Physisorption
Some of the important characteristics of physisorption are as follows:
(i) Deficient of specificity: since the van der Waal forces are universal, a given surface of adsorbent does not show any preference for any specific gas. It can adsorb all the gases but to a different extent.
(ii) Reversible nature: physical adsorption of a gas by the solid is reversible and thus equilibrium is reached rapidly
Solid + Gas 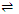 gas/solid + Heat
gas/solid + Heat
Thus, according to Le-chatelier's principle,
(a) Increase of pressure pushes the equilibrium in forward direction leading to more adsorption of gas and decrease of pressure cause desorption to occur.
(b) Since process is exothermic, therefore, lowering of temperature favours more adsorption and increase of temperature leads to desorption.
(iii) Surface area of adsorbent: the extent of adsorption increase with the increase of surface area of adsorbent. Thus, finely divided metals and rough surfaces are good adsorbents.
(iv) Nature of adsorbate: the amount of gas adsorbed by solid depends on nature of gas. In general, easily liquefiable gases (i.e gases with higher critical temperature) are readily as van der Waal forces are stronger near the critical temperature.
(v) Enthalpy of adsorption: the enthalpy of adsorption is low (20-40 kJ mol-1). This is because of weak nature of van der Waal's forces.
(vi) State of adsorbate: molecular state of adsorbate remains unaltered.
(vii) Activation energy: physical adsorption does not involve any chemical reaction and therefore, it requires very low activation energy.