Alcohols and phenols are the compounds containing one or more hydroxyl groups (- OH). The alcohols contain the -OH group attached to alkyl group whereas in phenols, the -OH group is attached to aromatic ring. These are classified as mono-, di- and trihydric alcohols or phenols according to the number of -OH groups contained in their molecules. Some examples of mono-, di- and trihydric alcohols and phenols are as follows:
Alcohols

It may be noted that the aromatic compounds in which -OH group is not directly attached to benzene ring are not phenols but are called aromatic alcohols. These may also be called as aryl derivatives of aliphatic alcohols. When four or more hydroxyl groups are present, they are called polyhydric alcohols or polyhydric phenols.
Monohydric alcohols may be further classified according to the hybrid state of the carbon atom to which the -OH group is attached.
Compounds containing Csp3 ) -OH bond
In this type of alcohols, the -OH group is attached to a sp3 hybridised carbon atom. They are further classify as follows:
Primary (1°), secondary (2°) and tertiary (3°) alcohols
Monohydric alcohols are classified as primary, secondary or tertiary alcohols depending upon whether the hydroxyl group is attached to a primary, secondary or tertiary carbon atom. For instance,
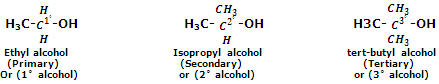
Allylic alcohols: in allylic alcohols, the -OH group is attached to a sp3-hybridised carbon next to the carbon-carbon double bond, that is to an allylic carbon. For instance,
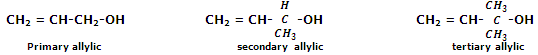
Benzylic alcohols: in benzlylic alcohols, the -OH group is attached to a sp3 -hybridised carbon atom next to an aromatic ring. Allylic and benzylic alcohols can be secondary, primary or tertiary.
Compounds containing Csp3 )-OH bond:
These alcohols include -OH group bonded to a carbon-carbon double bond i.e. to a vinylic carbon or to an aryl carbon. For example, vinylic alcohols and phenols belong to this class of compounds.