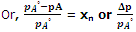The French chemist Francois Marie Raoult (1886) carried out a series of experiments to study the vapour pressure of a number of binary solutions. On the basis of the results of the experiments, he proposed a generalization called Raoult's law which states that,
The vapour pressure of a solution containing non-volatile solute is directly proportional to the mole fraction of the solvent.
In case of solution containing two components A (volatile solvent) and B (non-volatile solute) the vapour pressure of solution is given as
[Vapour pressure of solution] = [vapour pressure of solvent in solution (pA) ∝ [mole fraction of solvent (xA)]
Or pA ∝ xA
Or, pA = kxA
Where k is proportionality constant.
For pure liquid, xA = 1 then k becomes equal to be vapour pressure of the pure solvent which is denoted by pA°.
Thus, pA = pA°xA (i)
Or psolution × mole fraction of solvent.
For solutions obeying Raoult's law at all concentrations its vapour pressure would vary linearly from zero to the vapour pressure of pure solvent.
If mole fraction of solute is sB, then
xA + xB = 1 or xA = 1 - xB (ii)
From eqns. (i) and (ii),
pA = pA°(1 - xB) = pA° - pA°xB
Or, pA° - pA = pA°xB