Vander Waal's radii can be assigned to the atoms of molecules on the basis of the closeness of approach of these atoms in crystalline substances.
Diffraction studies of crystals give information about hoe molecules can approach each other and can pack together. Forces, often treated under the name vander Waal's forces, provide the attraction and repulsion between molecules that are responsible for the closeness with which molecules can approach other. The idea of a vander Waals radius for each covalently bound atom is introduced. The shapes attributed to molecules as a result of the introduction of vander Waals radii.
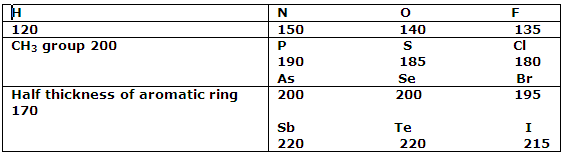
The values of these radii can be deduced from the distances that separate atoms in different molecules in a crystal lattice. In crystalline Br2, the shortest distance between a bromine atom of one molecule and that of an adjacent molecule is 390 pm. Half this value, 195 pm, can therefore be assigned as the van der Waals radius of a covalently bound bromine atom. In similar ways, by making use of crystal structure data for many organic compounds, the van der Waals radii can be deduced. These values must be considered reliable to not more than about 5 pm, and this uncertainty makes itself evident in the range of values found for a particular element in different compounds and crystals. The values are sufficiently reliable, however, for scale drawings to be constructed and used to see hoe molecules can fit together. That van der Waals radii can be assigned with some success is attributable to the fact, mentioned, that the repulsive forces set in very strongly i.e. the potential energy curve raised very steeply, as atoms approach each other. It follows that even when rather different attractive forces operate, the closeness of approach is affected little.