1. The units of Henry Law constant are same as those of pressure, i.e. torr or h bar.
2. Different gases have dissimilar values of Henry law constant. The values of KH for some gases in water are given in table below:
KH values of some gases in water at 298 K
|
Gas
|
kH (k bar)
|
Gas
|
kH (k bar)
|
|
H2
|
71.18
|
CH4
|
41.85
|
|
N2
|
86.78
|
CO2
|
1.67
|
|
O2
|
44.0
|
HCHO
|
1.83 × 10-5
|
|
Ar
|
40.3
|
CH2 = CHCl
|
0.611
|
3. The KH values of a gas are different in different solvents and it increases with the increase in temperature. For example the KH values of some gases in different solvents and also at different temperatures are given in table below:
KH values of some gases in different solvents and at different temperatures:
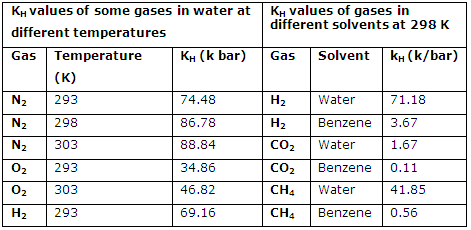
4. The knowledge of KH value of a gas at given temperature can help us in calculation of its solubility at the temperature. It is important to note that as the temperature is increased the solubility of gas decreases. This implies that higher the value of KH of a gas is, lower will be its solubility and vice versa.