The quantum mechanical methods, illustrated previously by the Schrödinger equation, are extended by the use of operators.
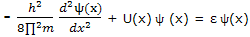
Or, with h for h/(2∏), as
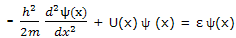
For each of the set of functions that satisfies this equation, the quantity ε is the energy of the particle in the state corresponding to that solution function.
This equation, with which the energy corresponding to each allowed state is calculated, is just one of a number of equations that can be set up to calculate properties of quantum mechanical systems. All these expressions can be looked on as operator equations. Equation can be displayed to show this feature by writing it as
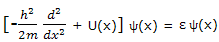
This expression in the square brackets is an example of an operator. This particular operator is one dimensional Hamiltonian operator. It or its two-or three-dimensional counterparts are given the symbol H. with this notation, equation can be written as
H ψ = ε ψ
Earlier we looked for functions that solved the Schrodinger equation, such as acted on by the operator H, give back a constant times the function. In this equation is the energy corresponding to that function. Functions that satisfy equations such as are known as eigenfunctoins, and the values of the constant, such as ε of equation are eigenvalues.
The energies of a system are identified as the eigenvalues for the Hamiltonian operator. Any other observable quantity has its own operator. The operator approach is therefore quite general. When an operator from an observable quantity operates on the wave function for the system and gives a result which is constant times the wave function, that constant is the value of the observable quantity.
Normalization: wave functions can be imaginary or complex, i.e. they can involve I = √-1. Let us now allow ψ to be such a function. Its complex conjucate, obtained by replacing I wherever it appears by -i, is denoted ψ *. A complex ψ is normalized if
∫ ψ * ψ d 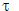 = 1
= 1
Example: normalize the wave functions for a particle on a line given as ψ = (const) sin (n∏x/a).
Solution: a wave function in one dimension is normalized if ∫ ψ * ψ dx= 1. Here we require that
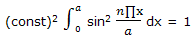
The integral can be simplified by introducing y = n∏x/a, so that
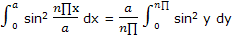
Now the integration result given in integral tables can be used to obtain
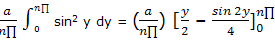
= (a/(n∏)) ((n∏)/2)
= a/2
It follows that (const) = (2/a)1/2 and that the normalized wave function is
ψ = (2/a)1/2 sin n∏x/a
Example: use the normalized wave function expression ψ = (2/a)1/2 sin (n∏x/a) for a particle-on-a-line and the position operator to obtain the expectation value for the position of a particle on a line segment.
Solution: the position operator is the x coordinate and the expectation value is given by equation here we have
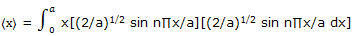
Substitution of y = n∏x/a converts this to

Use of the integration result from tables of integrals then gives
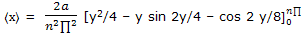
= 2a/(n2 ∏2 ) (n2∏2/4)
= a/2
We have come, by this formal procedure, to the result that the average, or expectation, value for the position of a particle on a line segment is at the middle of the segment. This result is apparent from symmetry of the wave functions.