The number of times each irreducible representation occurs in a reducible representation can be calculated.
Consider the C2v point group as described or Appendix C. you can see that (1) sum of the squares of the entries for each symmetry species is equal to 4, the number of operations, of the group; (2) the sum of the term-by-term products over all the operations for any two different symmetry species is zero. This example illustrates a general feature: the rows of point group tables' act as the components of orthogonal vectors do.
The vector-like property can be expressed mathematically. Let I refer to one row of the character table and j to another row. Let R represent any column of a character table. Thus R is a symmetry operation of any of the classes of symmetry operations. Let nR be the number of operations in the class. (This number is equal to the values in the first row of the character table.) You can verify for any of the character table of appendix C that
Σall classes nR 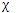 i(R)
i(R) 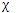 j(R) = {g i = j} {0 i ≠ j}
j(R) = {g i = j} {0 i ≠ j}
Where r is the number of symmetry operations in the group. The number g is known as the order of the group.
Example: verify that the rows, which give the characters of the different symmetry species, of the C3v character table of Appendix C, obey the relations.
Solution: the number of symmetry operations in the group, i.e. the order of the group, is obtained from the headings of the character table. Thus we obtain the value of g by adding 1 for the Esymmetry element, 2 for the C3 element, and 3 for the σv element, giving a total of 6.
First we test the i = j relation. We have
For A1: 1(1)(1) + 2(1)(1) + 3(-1)(-1) = 1 + 2 + 3 = 6
For A2: 1(1)(1) + 2(1)(1) + 3(-1)(-1) = 1 + 2 + 3 = 6
For E: 1(2)(2) + 2(-1)(-1) + 3(0)(0) = 4 + 2 + 0 = 6
In a similar way we can test the various i ≠ j possibilities. We have
For A1 and A2: 1(1)(1) + 2(1) (1) + 3(1)(-1) = 1 + 2 - 3 = 0
For A1 and E: 1(1)(2) + 2(1)(-1) + 3(1)(0) = 2 - 2 + 0 = 0
For A2 and E: 1(1)(2) + 2(1)(-1) + 3(-1)(0) = 2 - 2 + 0 = 0
The similarity of the characters of the various symmetry species to orthogonal vectors will lead us to the very useful relation. This equation enables us to calculate, for example, the number of molecular orbitals or the number of molecular vibrations that have the symmetry of the various symmetry species for the point group to which the molecule belongs. You might want to skip ahead to and become familiar with its use, rather than work through the development of this expression.
The idea that the characters ( 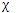 R) of any reducible representation are made up of the characters of some of the irreducible representation can be expressed by
R) of any reducible representation are made up of the characters of some of the irreducible representation can be expressed by
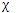 (R) = Σi aj
(R) = Σi aj 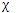 i(R), where for the class containing the Rth symmetry operation,
i(R), where for the class containing the Rth symmetry operation, 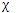 (R) represents the character for a reducible representation and
(R) represents the character for a reducible representation and 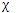 (R) represents the character for the jth irreducible representation, that in the jth row of the character table, occurs in the irreducible representation, or each row of the character table, occurs in a reducible representation. We focus on the jth row, and we attempt to find the value of ai. First we multiply both sides of equation by nR
(R) represents the character for the jth irreducible representation, that in the jth row of the character table, occurs in the irreducible representation, or each row of the character table, occurs in a reducible representation. We focus on the jth row, and we attempt to find the value of ai. First we multiply both sides of equation by nR 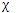 i(R), and then we sum over all classes of symmetry operations. We obtain
i(R), and then we sum over all classes of symmetry operations. We obtain
Σall classes nR 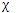 i(R)
i(R) 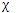 j(R) = Σall classes [nR
j(R) = Σall classes [nR 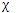 i(R) Σaj
i(R) Σaj 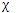 j(R)]
j(R)]
According to the right side will give zero contributions except when j = i. then the value of the right side is aj times g, where g is the order of the group. Thus
Σall classes nR 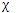 i(R)
i(R) 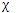 j(R) = ai g
j(R) = ai g
From above equation we write the important and useful relation
ai = 1/g Σall classes nR 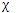 i(R)
i(R) 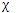 j(R)
j(R)