The average translational kinetic energies and speeds of the molecules of a gas can be calculated.
The result that the kinetic energy of 1 mol of the molecules of a gas is equal to 3/2 RT can be used to obtain numerical values for the average energies and speeds of these molecules. Notice, first, the remarkable generality of the relation KE = 3/2 RT. The translational kinetic energy of 1 mol of molecules, and therefore the average translational energy of the individual molecules, and therefore the average translational energy of the individual molecules, depends on only the temperature of the gas. None of the properties of the molecules not the atomic makeup, not the mass, not the shape-need is considered. The average kinetic energy of gas molecules depends on only the temperature.
Molecular translational energies: the value of R was obtained as 8.3143 J K-1 mol-1. The translational kinetic energy of 1 mol of gas molecules at 25°C (298.15 K) is
3/2 RT = 3/2 (8.3143 J K-1 mol-1) (298.15 K)
= 3718 J mol-1 = 3.718 kJ mol-1
This quantity, about 4 kJ/mol, will be a useful reference energy amount. It is a measure of the readily available, or "loose-change, " energy.
The average energy of a single molecule is given by
ke? = KE/ 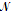 = (3/2 RT)/
= (3/2 RT)/ 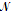
For dealing with the energies of individual atoms or molecules, it is convenient to introduce a constant k, called the Boltzmann constant, as
K = R/ 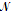 = 1.3806 × 10-23 J K-1
= 1.3806 × 10-23 J K-1
Notice that the Boltzmann constant is the gas constant per molecule. With this new constant we can express the average translational kinetic energy of a molecule of a gas as
ke? = 3/2 kT
This energy, at 25°C, is
ke? = 3/2 (1.3806 × 10-23 J K-1) (298.15 K)
= 6.174 × 10-23 J
Speeds of molecules: energies have broader application in chemistry than do speeds. But at first it is easier to appreciate speeds.
Consider a gas that contains molecules of a particular mass. Molecular speed values can be obtained by writing the kinetic energy of 1 mol of these molecules as
KE = 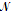 (1/2 mv2?) = ½(
(1/2 mv2?) = ½( 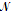 m)v2? = ½ Mv2?
m)v2? = ½ Mv2?
Where M is the mass of 1 mol of molecules. This kinetic energy is given, according to our kinetic-molecular theory deviation, by
KE = 3/2 RT
Equating these expressions and rearranging give
√v2 = √3RT/M
The cumbersome term √v2 is known as the root mean square (rms) speed. It is the value that would be obtained if each molecular speed were squared, the average value of the squared terms was calculated, and finally the square root of this average is obtained. The rms value is only slightly different from a simple average if the individual contributions are bunched closely together. The rms value is typically about 10 percent higher than the simple average. We can, for the moment, take the rms value as being indicative of the average molecular speed.
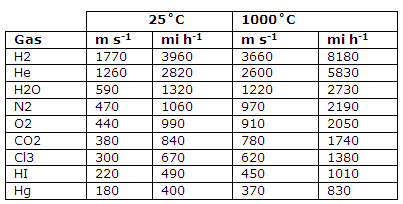
Average speeds of gas molecules (equal to 0.921 √v2) at 25°C (298 K) and 1000°C (1273 K)