For any symmetric object there is a set of symmetry operations that, together, constitute a mathematical group, called a point group.
It is clear from the examples that most molecules have several elements of symmetry. The H2Omolecule, for example, has the symmetry elements E, C2, σv, and σ'v. the sets of symmetry operations associated with such collections associated with such collections of symmetry elements are referred to as point groups. The mathematical implications of the word "group" are treated in the next section. The adjective "point" is used because the symmetry elements that are dealt with here leave a point of, or in, the molecule fixed in space. (point groups are in contrast to space groups. The latter are the collections of symmetry operations for which the operation consists of a transition of a unit cell to a new location in the crystal).
Now let us sample the variety of collections of symmetry elements and their associated symmetry operations. Each collections of symmetry operations constitutes a point group, and each point group is given a symbol. The symbol, written in boldface type, is usually based on the principle elements of symmetry of that point group.
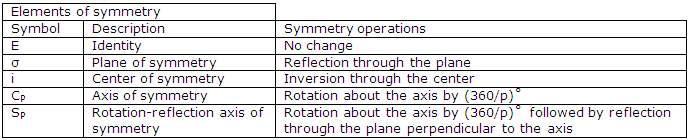
Simple symmetries: we begin the list of table with two point groups that are found when molecules with minimal symmetry are considered. For example, the bent molecule NOCl has only a plane of symmetry and the staggered molecule H2O has only a C2 axis of symmetry. Each, of course, has the identity symmetry element. Thus the point groups with symbols Cs and C2 which these examples suggest include only the identity operation and one other symmetry operation.
Single axis of symmetry: next we come to five collections of symmetry operations when we consider molecules with a single axis of symmetry. (This axis might have several rotational-symmetry operations associated with it.) The symbols for the point groups suggested by these molecules and the symmetry operations that constitute these groups in each of these point groups, the axis of rotation is taken to be the z axis. For a twofold axis the associated symmetry operation is a rotation by ½ revolutions. Since a threefold axis has two symmetry operations associated with it, the entry 2C3 (z) appears whenever there is a threefold axis. The symmetry operations associated with C4 indicated by 224(z) to indicate successive rotations by ¼revolutions. The planes associated with the symmetry operation of reflection are identified by thev, h, and d subscripts and, where appropriate, reference to the x, y, z coordinate system.
Principal and secondary axes: a set of rather more complex point groups, which will not br dealt with in detail. Each has the principal point group symbol D. the symmetry elements on which these point groups are based include axes that lie perpendicular to each other. The point groups for these collections of symmetry operations are referred to as the dihedral groups. Each point group symbol D has a subscript that shows the highest order rotation and suggests the types of planes of symmetry present.
Multiple principle axes: the tetrahedral molecules, such as CH4, and the octahedral molecules and ions, such as SF6, suggest two additional point groups, which, in spite of their complexity, should be introduced. Illustrations of the symmetry elements of such molecules are the symmetry operations of the tetrahedral point group Td and the octahedral point group OH, suggested by the collections of symmetry elements.
A total of about 27 point groups are found if the symmetry of all important molecular structures is investigated. Thus it provides only a sampling of important points groups. Some of the information will be used as individual molecules are studied. You need not attempt to master the table in advance of these studies.
The symmetry of a molecule can be described by specifying the symmetry elements of the molecule. Alternatively, and more simply, one can state the point group to which the molecule belongs. Thus, the entire symmetry of the H2O molecule is indicated by stating that the H2Omolecule belongs to the C2v point group. The symmetry of the CH4 molecule is indicated by saying that it belongs to the Td point group, and so forth.
Point groups have not been introduced simply to make such compact statements. Points groups are special combinations of symmetry operations, as you explore the special nature of these combinations we can learn about the symmetry features of the wave functions for the electrons of the atoms of the molecules, the wave functions for the electrons of the molecules, and the vibrations of the molecules belonging to any point group.