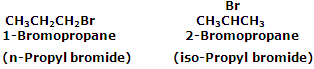In the common chemistry terminologies, aliphatic halogen derivatives are named as alkyl halides. The words, n-, sec-, tert-, iso-, neo-, and amyl are usually used in written in the common names. In IUPAC system, they are considered as derivatives of corresponding alkanes and are named as haloalkanes. It may be noted that the common name of any alkyl halide is written as two separate words whereas the IUPAC name of the alkyl halide is written as one word.
The dihalogen derivatives having same type of halogen atoms on the same carbon are known as germinal dihalides and are assigned common name alkylidene halides or alkylidene dihalides.
The dihalogen derivatives having the two similar halogen atoms on adjacent carbon atoms are known as vicinal dihalides and are assigned common name alkylene or alkylene dihalides.
Trihalomethnanes are called haloforms in trivial system.
Fully halogenated hydrocarbons are known as perhalohydrocarbons. For example, C2Cl6 is known as percholoroethane.
Haloarenes are named by prefixing the halogen and its position, if necessary, to the name of the parent aromatic compound.
In writing the common names, the relative positions of the substituents at 1, 2-; 1, 3- and 1, 4- positions are indicated by prefixes ortho (o-), meta (m-) and para (p-), respectively.
Isomerism in haloalkanes
Haloalkanes can exhibit the following kinds of isomerism:
Chain isomerism
The haloalkanes with four or more carbon atoms exhibit this kind of isomerism. For example,
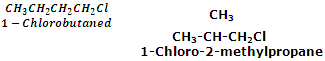
Position isomerism
The haloalkanes with three or more carbons show this kind of isomerism.
For example C3H7Br has two position isomers.