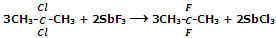Alkyl halides can be prepared from alkanes through substitution and from alkenes through addition of halogen acids or through allylic substitution.
From alkanes
When alkanes are treated with halogens, chlorine or bromine, in the presence of light or heat, they undergo free radical substitution and a mixture of mono- and poly- substituted products are obtained.
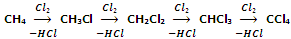
Although, the substitution beyond monohalogenation may be suppressed by using alkane in excess yet the method is not of much practical use because of the difficulties of separation of such a mixture.
In case of higher alkanes, different isomeric products are formed even when mono-substitution is carried out.
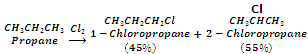
In general, the ease of substitution of different types of hydrogen atoms is:
Benzylic, allylic > tertiary > secondary > primary > vinylic, aryl
The iodination of alkanes is reversible and is done by heating with iodine in the presence of oxidising agents like conc. HNO3, HIO4 orHIO3. The function of using such agents is to oxidize HI formed during the reaction to iodine, and hence shift the equilibrium in the forward direction.
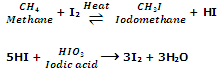
Due to formation of polysubstituted products and isomeric products, this method is not suitable for the laboratory preparation of pure haloalkanes. However, this method can be used for laboratory preparation of certain specific alkyl halides as given below:
When all the hydrogen atoms in the alkane are equivalent are equivalent, then it can form only one product on monosubstitution. In such cases this method may be applied.
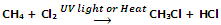
Allylic and benzylic halides can be prepared from alkenes and arenes respectively by this method because allylic and benzylic hydrogen atoms are substituted much more readily than vinylic and aryl hydrogen atoms.
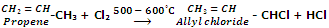
In such cases vinylic aryl hydrogens being less reactive do not participate in free radical substitution.
Allylic and benzylic hydrogen atoms are substituted very easily because their substitution proceeds via allylic and benzylic free radicals as intermediates. These intermediates are stabilized by resonance and hence being stable are formed at faster rate.
By halide exchange
Iodoalkanes can be obtained by treating bromo or chloroalkanes with a solution of sodium iodine in acetone or methanol. For example,
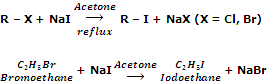
The reaction is known as Finkelstein reaction. This reaction is based on the fact that NaI is soluble in acetone but NaBr and NaCl are not. As a result, equilibrium in the above reaction is very much in favour of forward reaction. The reaction gives best result with primary halides.
Fluoroalkanes are difficult to prepare directly by the action of alkanes with fluorine. It is because fluoride has gor a high reactivity towards the hydrogen. It extracts all the hydrogen atoms from hydrocarbon molecule.
CH4 + 2F2  4HF + C
4HF + C
However, Fluoroalkanes can be obtained by treating alkyl halides with salts like AgF, Hg2F2, CoF3 or SbF3. This reaction is known as Swarts reaction.
CH3Br + AgF  CH3F + AgBr
CH3F + AgBr
2CH3CH2Cl + Hg2F2  2CH3CH2F + Hg2Cl2
2CH3CH2F + Hg2Cl2
For replacement of two or three halogen atoms at the same carbon CoF3 or SbF3 is used.