Basic character of amines is related to their structural arrangement. Basic strength of amines depends on the relative ease of formation of the corresponding cation by accepting a proton from the acid. Greater the stability of cation is, more is basic strength of amine.
Alkyl amines Verses Ammonia
Alkyl amines are stronger bases than ammonia. This can be explained in terms of electron releasing inductive effect (+I effect) of alkyl groups. Alkyl groups by their electron releasing effect, concentrate electron density on nitrogen and hence, make the lone pair of nitrogen more easily available for sharing with proton. Moreover, electron releasing effect of alkyl groups stabilizes the alkyl ammonia ion formed and hence, shifts the equilibrium in forward direction making the alkylamines stronger bases than ammonia.
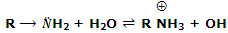
Variation of basic strength in primary, secondary and tertiary alkyl amines. Among primary, secondary and tertiary aliphatic amines, the electron releasing effect is maximum in tertiary amines and minimum in primary amines.
The basic strength is expected to increase from primary amine to tertiary amine. The observed basic strength of ethyl amine, diethyl amine and trimethyl amine have been found to follow the expected order in gas phase or in non aqueous solvents like chlorobenzene. However, the order of basicity in aqueous solution does not follow the expected trend and gets altered is revealed by their Kb values.
The actual order of basic strength among 1°, 2°, 3° methyl amines and ethyl amines is as follows:
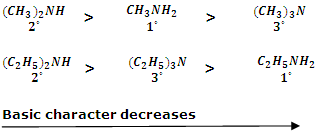
Why order of basic strength gets altered in aqueous medium?
In aqueous medium the basic strength of amines is determined by the stability of the corresponding conjugate acid, or protonated amine i.e. the ammonium ion formed by accepting the proton. The stability of the protonated amine is not only determined by the inductive effect but also by the hydration effect and steric factors.
Hydration effect: refers to the stabilization of the protonated amine by the water molecules water molecules form H-bonds with the protonated consequently, greater will be the basic strength of the corresponding amine. The hydration due to H-bonding is maximum in monoalkyl ammonium ion (protonated cation of 1° amine), it is less in dialkyl ammonium ion and still less in trialkyl ammonium ion. Therefore, basic strength should decrease from 1° > 2° > 3°.
Steric factors: refer to the crowding of alkyl groups around N atom which causes hindrance to protonation of amine and also cause obstruction to H-bonding of protonated amine. The steric effect obviously increase with the increase in the number of alkyl groups around N atom and consequently the basic strength of amines due to steric factors only should decrease from 1° > 2° > 3°.
The above discussion give us the conclusion that the basic strength of amines can be decided by the overall combined effect of I-effect, hydration effect and steric factors. All these factors favour the highest basic strength of 2° amine.
Now, if alkyl groups are small (such as - CH3 group), then steric hindrance to H-bonding is least. In this case, H-bonding predominates over the stability due to + I effect and therefore, CH3NH2 is more basic than (CH3)3N which corresponds to the observed order.
On the other hand, if alkyl groups are bulkier (-C2H5 and C3H7- etc). There will be considerable steric hindrance to H-bonding. Thus in this case + I effect predominates over stability due to H-bonding. Hence, in this case 3° amine becomes more basic than the 1° amine.