Polymers are the chief products of modern chemical industry which form the backbone of present society. Daily life without the discovery and varied applications of polymers would not have been easier and colourful. The materials made of polymers find multifarious uses and applications in all walks of our life. They have influenced our day to day life to such an extent that it is impossible to get through the day without using a material based on polymers. Common examples of these include plastic dishes, cups, non-stick. Pans, automobile tyres and seat covers, plastic bags, rain coats, plastic pipes and fitting radio, TV and computer cabinets; wide range of synthetic fibres for clothing, synthetic glues, flooring materials and materials for biomedical and surgical operations.
Word polymer means "many parts" (Greek: poly means many and merors means parts). A polymer is a compound of high molecular mass created by the mixture of large number of small molecules. The small molecules which comprise the repeating units in a polymer are known as monomer units. The process by which the monomers are transformed into polymer is called polymerization. For example, polyethylene is a polymer which is obtained by the polymerization of ethylene. The ethylene molecules are referred to as monomer units.
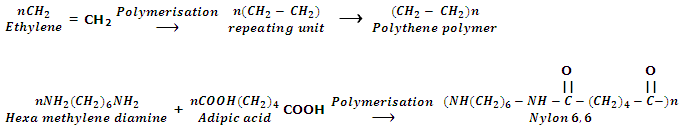
As polymers are single and giant molecules, i.e. big size molecules, they are also known as macromolecules.
Homopolymers and copolymers
Polymers are divided into two broad categories depending upon the nature of the repeating structural units. These are homopolymers and co-polymers.
The polymer formed from one kind of monomer is called homopolymers while polymer formed from more than one kind of monomer units is called copolymer or mixed polymer. For example, polyethylene is an example of homopolymers whereas Buna-S rubber which is formed from 1, 3-butadiene (CH2 = CH - CH = CH2) and styrene (C6H5CH = CH2) is an example of copolymer.