Haloalkanes are extremely reactive category of aliphatic compounds. Their reactivity is due to the presence of polar carbon-halogen bond in their molecules.
The chemical reactions of haloalkanes can be divided into four ways:
Nucleophilic substitution reactions
In haloalkanes, the halogen atoms are attached to the carbon atom. The bond between carbon and halogen is polar in character because the halogen atom is more electronegative than carbon.
Due to the presence of partial positive charge on the carbon atom, the nucleophilies can attack on electron deficient carbon thereby resulting the displacement of weaker nucleophile is generally stronger than it.
The order of reactivity of various alkyl halides towards nucleophilic substitution in the order:
Order of reactivity: RI > RBr > RCI > RF
This order of reactivity can be explained on the basis of strength of C-X bond. The C-X bond is the weakest in R-I and the strongest in R-F as is clear from the bond energy data for methyl halides. In fact, the C-F bond is so strong that organic fluorides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution under ordinary conditions.
|
Bond
|
C-I
|
C-Br
|
C-Cl
|
C-F
|
|
Bond Enthalpies (kJ/mole)
|
234
|
293
|
351
|
452
|
|
Bond length (pm)
|
214
|
193
|
178
|
139
|
|
Dipole moment (Debye)
|
1.636
|
1.830
|
1.860
|
1.847
|
Examples of nucleophilic substitution reactions of haloalkanes
Replacement of hydroxyl group (Formation of alcohols).
Haloalkanes on treatment with aqueous solution of KOH or moist silver oxide (Ag2O/H2O) give alcohols.
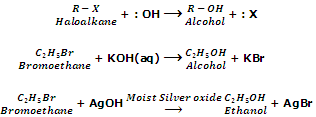
Replacement Alkoxy group (Formation of ethers). (Williamson Synthesis):
Haloalkanes on treatment with alcoholic sodium or potassium alkoxide form ethers. This reaction is called as Williamson Synthesis.
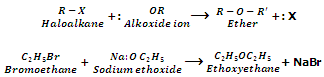
Ethers can also be prepared by heating alkyl halides with dry silver oxide, Ag2O
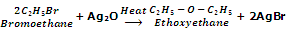
Replacement by Cyano Group (Formation of cyanides or nitrites)
Haloalkanes on treatment with alcoholic KCN solution give alkanenitriles or alkyl cyanides as the major product with a small amount of alkyl isocyanide.
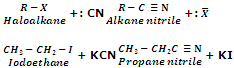
The reaction of alkyl halides with KCN gives us an important method for increasing the length of carbon chain by one carbon atom i.e. rising of series.