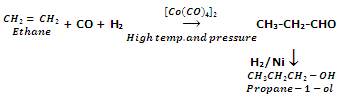The important methods for the preparation of alcohol on large-scale are given below:
By hydration of Alkenes
Alkenes are obtained by cracking of petroleum. They are easily converted to alcohols by the addition of water in presence of sulphuric acid.
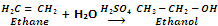
In case of unsymmetrical alkenes, the addition takes place according to Markowniko's rule.
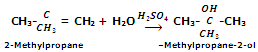
By fermentation of carbohydrates
Formation of ethyl alcohol by the fermentation of sugar (obtained from molasses, grapes or beet) is one of the oldest methods. Sucrose is first of all changed to glucose and fructose with an enzyme invertase.
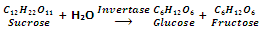
Enzyme zymase after that converts glucose and fructose into ethanol.
The enzyme zymase is present in yeast.
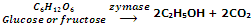
The fermentation procedure is taken out under anaerobic conditions i.e. in the nonexistence of air. Carbon dioxide released during fermentation keeps the fermentation mixture out of contact of air. If the fermentation mixture gets exposed to air, the oxygen of air oxidizes ethanol to ethanoic acid which makes the mixture sour.
Ethanol is obtained from starchy materials such as barley, rice, maize and potatoes with enzymes diastase and maltase.
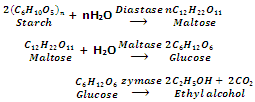
Enzyme diastase is obtained from germinated barley while enzyme maltase and zymase are obtained from yeast.
Oxo process
Alkenes react with carbon monoxide and hydrogen in the presence of Octacarbonyl dicobalt Co[CO]