The integrated forms of the first order rate equations are conveniently used to compare concentration time results with this rate equation.
Rate equations show the dependence of the rate of the reaction on concentration can be integrated to give expressions for the dependence of the concentrations on time. We generally use the integrated rate equation that is obtained to deduce the order of a reaction.
A first order reaction is one for which, at a given temperature, the rate of the reaction depends only on the first power of the concentration of a single reacting species. If the concentrations of this species is represented by c (for solutions, the units of moles per litre are ordinarily used), and if the volume of the system remains essentially constant during the course of the reaction, the first order rate equation can be written
-dc/dt = kc
The rate of constant k is then a positive quantity and has the units of the reciprocal of time.
Integrated rate equation: the experimental results obtained in a study of the rate of a reaction are usually values of c or some related to c at various times. Such data can best be compared with the integrated form of the first order rate equation. If the concentration at time t = 0 is c0, and if at some later time t the concentration has fallen to c, the integration gives
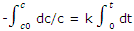
With -In (c/c0) = In (c0/c), the integration can be written as
In c0/c = kt
Sometimes a more convenient form is
In c = -kt + In c0
A reaction can therefore be said to be first order if a plot of In (c0/c) or In c versus t gives a straight line. If a straight line is obtained, the slope of the line can be used to give the value of the rate constant k. an alternative to this graphical procedure is the calculation of a value of kfrom the individual measurements of c at the various times t, for example. The reaction is classified as first order if all the data lead to essentially the same values for k, that is, if it is satisfies with k as a constant.
Example: the rate of conversion of tert-butyl bromide to tert-butyl alcohol, (CH3)3CBr + H2O 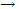 (CH3)3COH + HBr, has been studied and some concentration-time results are found in table given below. Verify that the reaction is first order, and deduce the values of the rate constant at the two temperatures.
(CH3)3COH + HBr, has been studied and some concentration-time results are found in table given below. Verify that the reaction is first order, and deduce the values of the rate constant at the two temperatures.
Solution: from the data at each temperature we calculate In (c0/c) values. Then the graphical display shows a plot of In (c0/c) versus t is constructed. The straight lines, each going through the origin show that at both temperatures the data conform to the integrated first order relation. The slopes give the values of the rate constants
K = 0.00082 min-1 = 0.137 × 10-4 s-1 [25°C]
K = 0.0142 min-1 = 2.37 × 10-4 s-1 [50°C]
Concentration of tert butyl bromide as a function of time for the reaction (CH3)3CBr + H2O 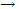 (CH3)3COH + HBr in a 10% water, 90% acetone solvent
(CH3)3COH + HBr in a 10% water, 90% acetone solvent
| Time, h |
(CH3)3CBr, Mol L-1 |
Time, min |
(CH3)3CBr, Mol L-1 |
| 0 |
0.1039 |
0 |
0.1056 |
| 3.15 |
0.0896 |
9 |
0.0961 |
| 6.20 |
0.0776 |
18 |
0.0856 |
| 10.0 |
0.0639 |
27 |
0.0767 |
| 13.5 |
0.0529 |
40 |
0.0645 |
| 18.3 |
0.0353 |
54 |
0.0536 |
| 26.0 |
0.0270 |
72 |
0.0432 |
| 30.8 |
0.0207 |
105 |
0.0270 |
| 37.3 |
0.0142 |
135 |
0.0174 |
| 43.8 |
0.0101 |
180 |
0.0089 |