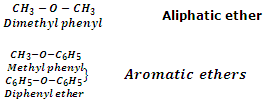Ethers are the compounds with general formula or CnH2n+2O (same as monohydric alcohols). These are symbolized through a general structure. R-O-R'. They may be regarded as dialkyl derivatives of water or mono alkyl derivatives of alcohols.
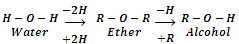
They are also considered as anhydrides of alcohols because they can be obtained by the elimination of water molecule from two alcohol molecules.
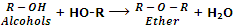
The groups R and R' in ether may either be same or different. In case these groups are same, the compounds are known as simple ethers or symmetrical ethers. On the other hand, if R and R' groups are different, the compounds are called mixed ether or unsymmetrical ethers.
C2H5-O-C2H5 Simple ether
C2H5-O-CH3 Mixed ether
Ethers may also be classified into two categories as aliphatic ethers and aromatic ethers. In aliphatic ethers, the groups R and R' are both alkyl groups whereas in aromatic ethers, one or both R and R' groups are aryl groups. Ether with one alkyl and one aryl groups are also called aryl alkyl ethers or phenolic ethers whereas ethers with both aryl groups are called diaryl ethers. Few examples are taken below: