To meet human needs, scientists have started preparing synthetic rubbers. Besides having similar properties as natural rubbers they are tougher, more flexible and more durable than natural rubber. They are capable of getting stretched to twice its length. Though, it reverts to its original shape and size once the external stretching force is released.
Synthetic rubbers have been made by the polymerisation of dienes other than isoprene. The polymerisation is carried out in the presence of Zeigher-Natta catalyst. For example, Polymerisation of 1, 3-butadiene
Preparation of synthetic rubbers
1. Neoprene or polychloro prene is formed by the free radical polymerisation of chloroprene.
It has superior resistance to vegetable and mineral oils. It is used for manufacturing of conveyer belts, gaskets and hoses.
2. Buna-N: you have previously studied about Buna-S. Buna-N is obtained by the copolymerization of 1, 3-butadiene and Acrylonitrile in the presence of a peroxide catalyst.
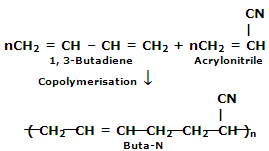
It is resistant to the reaction of petrol, lubricating oil and organic solvents. It is utilized in making oil seals, tank lining etc.