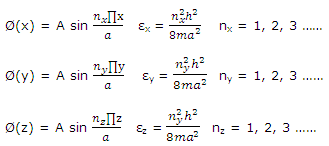Three dimensional applications of the Schrodinger equation are introduced by the particle-in-a-box problem.
So far only a one-dimensional problem has been solved by application of the Schrodinger equation. Now the allowed energies and the probability functions for a particle that is free to move in three dimensions are deduced. A molecule of a gas enclosed in a cubic container provides a specific example that is dealt with in the section after the general procedure has been developed.
For any three-dimensional problem, the potential energy is, general, a function of three coordinates. For a cubic potential box, the Cartesian coordinates are convenient. The differential equation that must be solved is now the Schrodinger equation in three dimensions.
For a "cubic box," the potential function can be expressed in terms of separate x, y, and z components,
Each of the potential function components for a "particle-in-a-box" is like the one-dimensional potential for a "particle-on-a-line".
For three-dimensional systems, the solution function ψ depends on the three coordinates necessary to locate a point in space. It is often profitable to try to separate such systems into parts, with each part involving only one coordinate. On the basis we try the substitution
ψ (x, y, z) = Ø(x)Ø(y)Ø(z)
Substitution of (2) from (1) gives
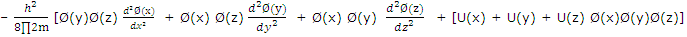
Division by Ø(x)Ø(y)Ø(z) gives
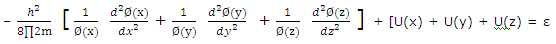
For the equation to be satisfied for all values of x, y and z, each term on the left must equal a component of ε, and we can write
ε = εx + εy + εz
The Schrodinger equation can then be broken down into three identical equations of the type
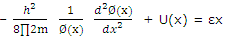
Or
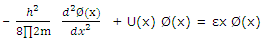
These equations are identical to that written for one-dimensional problem. The solution to the three-dimensional cubic-box problem is therefore
ψ = Ø(x)Ø(y)Ø(z)
With