Integration of the second order rate equations also produces convenient expressions for dealing with concentration time results.
A reaction is classified as second order if the rate of the reaction is proportional to the square of the concentration of one of the reagents or to the product of the concentrations of two species of the reagents. The second situation leads to the same equations as the first if the two reactants are used up at the same rate and if their initial concentrations are equal.
Rate = kc2. For these situations, the rate equation is
-dc/dt = kc2, where c is the concentration of the single reagent or one of the two reagents. Again the kinetic data are usually compared with the integrated form of the equation. One has
- 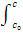 dc/c2 = k
dc/c2 = k 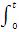 dt
dt
And
1/c - 1/c0 = kt
A reaction of the types considered so far is therefore second order if a plot of 1/c versus t gives a straight line. The slope of the straight line is equal to the rate constant. Equation shows, this constant involves the units of concentrations, differing in this respect from the first order rate constant that involves only the units of time. Furthermore, the time for the concentration to drop to half its initial value is deduced from equation to be
t1/2 = 1/kc0
The half life therefore depends on the initial concentration and is not a convenient way of expressing the rate constant of second order reactions.
Example: use of second order half life expression to verify that the rates used which were obtained for periods of reaction up to about 30 min, were indeed "initial rates".
Solution: although the concentrations of the two reactants, iodine ions and peroxydisulfate ions, reported are somewhat different we can use a representative value of 0.01 mol L-1. Then with k = 0.36 mol-1 L min-1, gives
t1/2 = 1/(0.36 mol-1 L min-1) (0.01 mol L-1)
= 300 min
About half the reactants would be used up in 300 min. since the reaction was studied only in times up to about 10 min, the initial concentration could not have changed appreciably. The method of initial rates was applicable.
Rate = kcA cB: instead of working with the concentration of the reacting species, as was done with previous equation, it is more convenient to develop the rate equation by introducing a term for the amount of reaction that has occurred at time t. the overall reaction might, for example, be of the form
A + B 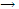 products
products
If it is inconvenient to arrange to have the initial concentrations of A and B equal the analysis that led to equation cannot be used, but the kinetic data can be treated in terms of the following quantities:
a = initial concentration of A
b = initial concentration of B
X = decrease in A or B at time t = amount of product at time t
a - x = concentration of A at time t
b - x = concentration of B at time t
The differential second order rate equation would then be
dx/dt = k[A][B] = k(a - x)(b - x)
The integration can be performed by using partial fractions. Thus
dx/(a - x)(b - x) = k dt
leads to the integral
1/a - b 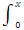 (- dx/a - x + dx/b - x) = k
(- dx/a - x + dx/b - x) = k 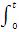 dt
dt
On integration this gives
1/a - b [In (a - x) - In (b - x)]0x = kt
Insertion of the limits and rearrangement give, finally,
1/a - b In b(a - x)/a(b - x) = kt