The equation S = k in W relates entropy to W, a measure of the number of different molecular level arrangements of the system.
In the preceding developments it was unnecessary to attempt to reach any "explanation" of entropy. But the history of chemical shows that we get great insight into, and control over, the material word then we seek and develop a molecular level interpretation of properties and phenomena. It is not immediately obvious what molecular phenomenon is responsible for the entropy of a system. Some idea of what should be calculated can be obtained by tying to discover a quantity that would tend to increase when an isolated system moves spontaneously toward the equilibrium position. A very non chemical example will reveal such a quantity.
Consider a box containing a large number of pennies. Suppose, further, that the pennies are initially arranged so that they all have heads showing. If the box is now shaken, the chances are very good that some arrangement of higher probability, with a more nearly equal number of heads and tails, will result. This system of pennies has, therefore, a natural, or spontaneous, tendency o go from the state of low probability to one of high probability. The system can be considered to be isolated since no energy is transferred, and the shaking process could almost be presented by using some other objects that could turn over more easily. The deriving that operates in this isolated system is seen to be the probability. The system tends to be change towards its equilibrium position and this change is accompanied by an increase in the probability. Such an example suggests that the entropy might be identified with some functions like probability. The next sections will show in more detail that the entropy is quantitat
vely related to the probability.
Now consider a slightly more chemical example. Consider the equilibrium of A and B in which B molecules have more available quantum states than do A molecules. There then more ways of distributing the atoms in these states so that the molecules of type B are formed then there are ways of arranging the atoms in that a molecule of type B, even if no energy driving force exists, is therefore understood to be due to the driving force that takes place the system from a state of lower probability of few quantum states and few possible arrangements, to one of higher arrangements. The qualitative result from this discussion is: a substance for which the molecules have and therefore the higher number of molecular level arrangements and therefore the higher entropy.
The molecular explanation of the entropy change in the system is basically quite simple. In practice, of course, it is not always easy to see whether a process or reaction, produces a system with more, or less, available quantum states or energy levels. For example, for the liquid to vapour transition a large entropy increase occurs. The difficult encountered in a molecular understanding of the liquid state make it very difficult to evaluate this entropy increase from the molecular model.
Entropy and the number of molecular level arrangements: the headstone on Ludwig Boltzmann's grave has the inscription:
S = k In W
The inscription does not go on to say, "where k, now known as Boltzmann's constant, is the gas constant per molecule-level arrangements that the particles can adopt for the specific macroscopic state."
The relation S = k In W boldly relates S, a macroscopic property, to W, a molecular-level quantity. It is an elegant display of the chemistry. You will accept it, and appreciate it, as we use it to calculate entropies and compare the results with the values based on calorimetric relation.
The general relation for W was developed after a "marbles-in-boxes" analysis, we arrived at the relation:
W = (g1N1 g2N2 g3N3...) 1/N1! N2! N3!...
And in W = Σ Ni In gi - Σ In Ni!
With Sterling's approximation In (x!)
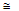 In x - x, which is valid for large numbers, this expression for In W can be recast as:
In x - x, which is valid for large numbers, this expression for In W can be recast as:
In W = Σ Ni (1 + In gi/Ni)
We want an expression for In W for the Boltzmann distribution. The most convenient form of this distribution is given, for an Avogadro's number of particles, written as:
Ni/gi = N/q e- (ε1 - ε0)/(kT)
Where q is the partition function, clearly to develop we need the logarithm of the reciprocal of this Boltzmann expression. This is:
In gi/Ni = ε1 - ε0/kT + In q/N