Nitrogen tetroxide (melting point: -11.2°C, normal boiling point 21.15°C) decomposes into nitrogen dioxide according to the following reaction:
N2O4(g) ↔ 2 NO2(g)
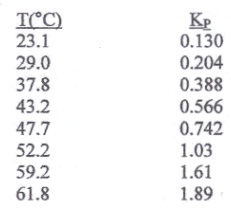
The decomposition reaction is fast and the color of the gas goes from clear to brown as the extent of dissociation increases. Using only the experimental data presented below, answer the following questions.
a) Is the decomposition reaction endothermic or exothermic? Why?
b) What is the extent of dissociation at 61.8°C and 1 bar if the initial state consists of pure N2O4?
c) Repeat part (b) for the case where the total pressure is 0.5 bar.
d) Repeat part (b) for the case where the initial state consists of 50 mol% inerts and 50 mol% N2O4.
e) Determine Δhorxn at 47.7°C.
f) Determine Δgorxn, at 47.7°C
g) Determine Δsorxn, at 47.7°C
Data: