Polyatomic molecules vibrate in a number of ways, and some of these vibrations can be studied by infrared absorption spectroscopy and some by Raman spectroscopy.
The characters of transformation matrices for all 3n translation rotation vibration motions of a molecule can be deduced by using the three Cartesian coordinates at each atom as a basis. TheH2O example led us to except two vibrations of symmetry A1 and one of symmetry B1.
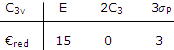
As a second example worked out in vibrations of these types are repeated with the symmetry fo the molecule is C3v. the 3n Cartesian displacement vectors are shown in the recipes for the characters given in the table under:
The CH3Cl molecule has three totally symmetric A1 vibrations and three pairs of doubly degenerate E vibrations. These can be pictured and identified with absorptions.
The A1 vibrations have associated with them an oscillating dipole that is directed the unique z, axis. Such vibrations of symmetric top molecules are described as parallel.
Symmetry and infrared and roman spectra: oscillating dipole components have the same symmetry properties as the x, y, z vectors displayed alongside character tables. The rows in which x, y, zoccurs give the symmetry types for the three components of the oscillating dipole. In both theH2O and CH3Cl examples, all vibrations are infrared active. In more symmetric molecules some vibrations will have a symmetry type other than those symmetric corresponding to the rows containing the vectors. Such vibrations will be infrared inactive they will produce no absorption of radiation.
Symmetry considerations also lead to conclusions about the vibrations of symmetric molecules that are Roman-active. The distinction between Raman and infrared activity can most easily be seen by considering a molecule with a center o symmetry. A simple example is provided by the CO2molecule vibrations are only those vibrations which remove the symmetry with respect to the center of symmetry can create an oscillating dipole moment. Thus only the second and third vibrations are infrared active. Raman activity can be deduced by seeing which distortions could lead to an oscillating polarizability. You can assume that stretching a bond changes the polarizability in one way and compressing it changes the polarizability to the same extent but in the opposite way. Then you expect only the first vibration to be Raman-active.
The deduction illustrates a general rule. If a molecule has a center of symmetry, only those vibrations which are antisymmetric with respect to the center can be Raman-active.
Characteristic frequencies: a more detailed analysis of the dependence of polarizability on molecular distortions would show that Raman activity occurs only for vibrations with the symmetry of any type of square or cross product terms of character tables. You can use this guide and the character table.
In a practical use of great value, particularly in organic chemistry, the infrared absorption spectrum of a large molecule is used to identify the compound or to indicate the presence of certain groups in the molecule. Bonds or groups within a molecule sometimes vibrate with a frequency, i.e. have an energy level pattern with a spacing that is little affected by the rest of the molecule. Absorption at a frequency characteristic of a particular group can then be taken as an indication of the presence of that group in the compound being studied.
An even simpler use of vibrational spectra consists of a compound by matching its spectrum to that of known sample. Large molecules have such complicated spectra can be taken as a sure indication of identical compounds. Thus, although for large molecules the complete vibrational spectrum can be understood in terms of the nature of the vibrations, there are many uses in which such spectra can be put.