Assignment:
I: Questions
1) You discover an Earth-like planet around another star (50 light years away from Earth) with the same mass and diameter as the Earth. You determine that it takes 400 days for the planet to make one orbit around the star. One scientist says that the planet has to have semi-major axis that is greater than 1 AU. Another scientist corrects him and says that it is possible for the planet to have a semi-major axis of less than 1 AU. How could the second scientist be correct?
2) Your friend says there is a star with an azimuth of 8 degrees, altitude of 74 degrees, and an apparent magnitude of 2.0 in the sky at 10:00 pm on July 28, 2014in South Hadley. It is a perfectly clear night. Should you be able to see this star in South Hadley on July 28, 2014at 10:00 pm using just your eyes? Why or why not?
3) In movies, planets appear to have the same acceleration of gravity as the Earth. Would you typically expect this be true for planets in our galaxy? Give a reason to support your answer.
4) If you are floating in space, is the force of attraction between you and the Earth exactly zero? Why or why not?
5) You travel to another star system and meet some aliens. They say there are 50 constellations in the sky and not 88? Why would they say this?
6) Somebody says the reason the Earth has seasons is because the Earth is closer to the Sun during the summer and farther away during the winter. Is this person correct? If the person is incorrect, give a reason why that person is incorrect.
7) A photon has a wavelength of 3 meters. What is this photon's frequency and energy? What part of the electromagnetic spectrum does this photon fall in? Where are the telescopes that observe this part of the electromagnetic spectrum usually located? Why?
8) A 20-km asteroid isdiscovered by a spacecraft to currently be on the exact opposite side of the Sun from the Earth so it is currently not observable with telescopes on Earth. It is in a counter-clockwise orbit around the Sun. It has a semi-major axis of 1.0 AU and its orbit is almost completely circular with an eccentricity of 0.0167. Would you expect this asteroid to be ever visible in the skywith a telescope from Earth? Why or why not?
9) Do you think Eris should be considered a planet? Why or why not? Give two reasons for your opinion.
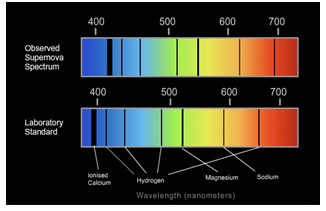
10) The bottom spectrum contains spectral lines measured in a laboratory while the top spectrum contains spectral lines measured for a supernova (exploding star). Are the star's spectral lines redshifted or blueshifted? How do you know for sure? Estimate the velocity the supernovaappears to be moving away or towards you
11) What are two reasons why one star may appear brighter than another star in the sky on a perfectly clear night?
12) A newly discovered element has an atomic number of 114 and an atomic mass of 289. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons does a neutral atom of this element have?
13) An asteroid takes 12 years to orbit the Sun. What is its semi-major axis?
14) Why can radio telescopes be located on the surface of the Earth while gamma-ray telescopes are not?
15) Why do people say when you are looking at galaxies, you are looking backwards in time?
16) An object is 200oC. What is this temperature in Kelvin? What would happen to water at this temperature on the surface of the Earth?
17) What are two problems with building a refracting telescope with a 2-meter diameter lens?
18) Over the summer, you see an object travelling through the constellation Orion. Could it be one the eight planets?
19) In a perfect vacuum, would you expect visible wavelength photon or a gamma-ray photon to travel faster? Why or why not?
20) What would have a larger force on you when you were born: a doctor in the delivery room or the star Sirius.Show all calculations for full credit.
21) Why was Pluto considered a planet when it was discovered in 1930 but is now considered a dwarf planet? Be detailed in your answer.
22) Would you expect a star that appears red in the sky to have a hotter surface temperature than the Sun or a cooler one? Why?
23) If you can travel at the speed of light, approximately how long will it take you to travel to the star Sirius (8.611 light years away)?
24) Why has the number of known planets in our solar system changed over the last ~200 years?
25) Name one thing that you have learned so far in the class that you didn't know before.
II: Questions
1) A black hole has a mass that is 10,000 times the mass of the Sun. What is its Schwarzschild radius? Show all work for full credit.
2) A Cepheid Variable star has a period of 10 days. What is its luminosity?
3) A main sequence star has a mass of 8 solar masses and a luminosity of 1,000 solar luminosities. What is its main sequence lifetime? Show all work for full credit.
4) Why aren't Type II (core collapse) supernovae used as standard candles while Type Ia supernovae are used as standard candles?
5) Carl Sagan once said "We are Star-Stuff". What did he mean?
6) A number of particles are produced during the fusion reaction in the Sun. What particles are produced and what happens to the particles after they are created (their final fate)?
7) Put these main sequence stars (A2, B4, F6, G9, O8, M5) in order of increasing surface temperature, increasing mass, and increasing main sequence lifetime.
Low → High Temperature
Low → High Mass
Short → Long Main Sequence Lifetime
8) What is the main deciding factor whether a main sequence star becomes a white dwarf, neutron star, or black hole? Why?
9) How can you use the Hydrogen 21-cm line transition to measure the rotation curve of a galaxy?
10) Why are Cepheid Variables used as standard candles?
11) How would you estimate the number of stars in a galaxy?
12) Why do we think most of the mass of our galaxy is made of dark matter?
13) If 10% of the mass of the Sun is hot enough to undergo fusion into Helium during its lifetime, how much energy will be produced?
14) Why doesn't fusion occur on the surface of the Sun?
15) Show how you would estimatehow many planets exist in the universe. Explain all parts of your calculation. Give your estimate.
16) What are two pieces of evidence that the Big Bang occurred?
17) Why won't our Sun become a Type Ia supernova?
18) What is evidence that galaxies merge together?
19) Why do we think life could have existed on Mars?
20) Why do we think pulsars are rotating neutron stars?
21) A galaxy has a recession velocity of 100,000 km/s and follows Hubble's Law. How far away is the galaxy from Earth? Show all work for full credit.
22) How is Hubble's Constant calculated?
23) Using the Drake Equation, estimate the number of communicating civilizations in the galaxy. Explain what all the variables mean and the values you use. Pick realistic values.
24) Give 10 solutions to the Fermi Paradox.
25) How much energy is released when a positron and aan electron collide? Show all work for full credit.
26) Name one thing that you learned in the last half of class that you didn't know before.