Binary Choice Section
Use the following diagram to answer the next 2 questions . In this graph the horizontal axis measures BMWs (a type of car) while the vertical axis measures total cost in dollars.
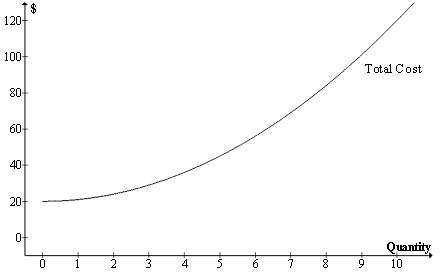
Question 1. According to the diagram, as the total cost of producing BMWs increases, the marginal cost of producing an additional BMW
a. Increases
b. Decreases
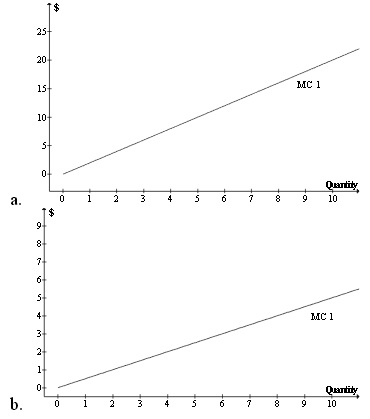
Question 2. Which of the following marginal cost curv es would correspond to the total cost curve given
Question 3. Suppose in the market for automobiles, in the open economy of the United States, the domestic demand curve is linear and downward sloping while the domestic supply curve is linear and upward sloping. Assume the world price of automobiles is lower than the closed market domestic equilibrium price in the United States. Which of the following statements is correct?
a. Since the imposition of a tariff will make the price in the United States higher than the world price, the imposition of a tariff will result in foreign producers earning higher profits in th e United States than they earn in other countries.
b. The imposition of a tariff on automobiles in the open economy of the United States will result in an increase in domestic production of automobiles in the United States.
Question 4. Sammy considers 2 wooden pencils to be a perfect substitute for 1 mechanical pencil. The price of 1 wooden pencil is $2, and the price of 1 m echanical pencil is $3. Sammy has an income of $18. Wh at is Sammy’s optimal consumption bundle?
a. 0 wooden pencils and 6 mechanical pencils
b. 9 wooden pencils and 0 mechanical pencils
Question 5. Suppose as output increases for a firm, margin al cost is greater than average total cost. This means that
a. Average Variable Cost is increasing.
b. Average Variable Cost is decreasing.
Question 6. Which of the following is not a requirement for a perfectly competitive industry?
a. All consumers have full information on the price charged by each firm.
b. Each firm in the industry recognizes th at the quantity of output it produces can affect the equilibrium price.
Question 7. The goal of most firms is to maximize th eir total revenue by se tting the price of their good at that price where the price elasticity of demand for the good is equal to 1.
a. True
b. False
Question 8. Consider the typical linear downward sloping domestic demand curve and linear upward sloping domestic supply curve for a certain good. Is the following statement true or false for this good? “The total surplus for this market when it opens to world trade without any governme nt invention can not be smaller than the total surplus for this market when it is closed to world trade.”
a. True
b. False
Question 9. The inflation rate for 2007 is reported as 4.5% w hile your nominal wage increases by 2.25% during the same period. Which of the following statements is true?
a. Your purchasing power has increased.
b. Your purchasing power has decreased.
Question 10. If the price elasticity of demand is cons tant everywhere along the demand curve, then the slope of the demand curve is constant.
a. True
b. False
Question 11. Which of the following products is most likely not included in the basket of goods used to calculate CPI?
a. John Deere Industrial Tractor
b. Pontiac G8 Sedan
Question 12. Suppose a consumer buys two goods: suga r and paprika. The consumer has a typical indifference curve for the two pr oducts. Assume paprika is an inferior good, but sugar is a normal good. This implies _____________.
a. Sugar and paprika are substitutes
b. Sugar and paprika are complements
Multiple Choice Section
Use the following diagram to answer the next question :
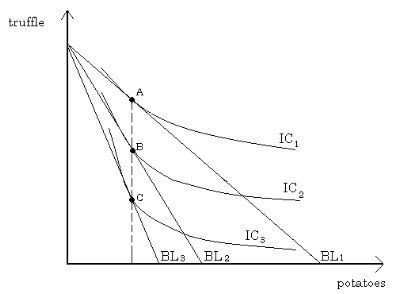
Question 13. According to the figure, it is possible to say that:
a. The demand for truffles is perfectly inelastic.
b. The demand for potatoes is perfectly elastic.
c. The price of truffles is changing.
d. The demand for potatoes is perfectly inelastic
Question 14. A profit-maximizing firm will
a. Exit the industry in the long run if the price is above the shut-down price.
b. Exit the industry in the short run if the price is below marginal cost, but above average fixed cost.
c. Exit the industry in the short run if th e price is below the break-even price.
d. Exit the industry in the l ong run if the price is belo w the break-even price.
Question 15. The CPI in 2006 was 80 and the CPI in 2008 was 120. Terry bought a car in 2006 for $8,000, and sold the car in 2008 for $6,000. What is the r eal price of the car in 2008 using 2006 as the base year?
a. $2,000
b. $3,000
c. $4,000
d. $4,500
Use the following information to answer the next 3 questions :
The domestic supply curve of coffee in the Un ited States is P = 2Q + 6 when the market is closed to world trade. The domestic demand curve in the United States is P = 21 - Q when the market is closed to world trade. Suppose the world price of coffee is $8 and the market for coffee in the United States is now opened to world trade.
Question 16. The government implements a quota policy in the market for coffee that allows the license holder to import 3 units of coff ee. What is the supply curve for coffee given this quota (assume this is the supply curve for price equal to or greater than $8)?
a. P=2Q+9
b. P=0.5Q
c. P=0.5Q-3
d. P=2Q
Question 17. Suppose the government sells the license to import 3 units of coffee. In selling these licenses, the government sets the pri ce so that the government extracts the entire surplus earned by the license holders. How much does the government expect to earn from the sale of the license?
a. $14
b. $16
c. $18
d. $20
Question 18. Assume there is no quota and the governme nt enacts a tariff to ensure domestic producers are able to earn exactly $4 in producer surplus. How much tariff is necessary for domestic producers to ear n this am ount of producer surplus?
a. $0.5
b. $1
c. $1.5
d. $2
Question 19. Suppose the electricity industry is a natura l m onopoly with constant marginal cost. The government wants to protect the consumers given the monopoly power in the electricity industry. The government theref ore regulates the market price to be equal to marginal cost in this industry since the government knows that price is always equal to marginal cost in a perfectly competitive industry. What will happen in the long run in the electricity industry?
a. The electricity provider will charge its marginal cost as the price and increase production.
b. The electricity provider will charge its marginal cost as the price and decrease production.
c. The electricity provider will charge its marginal cost as the price and keep production the same.
d. The electricity provider will exit out of the industry.
Question 20. Suppose that the CPI in Japan was 200 in 2000 and that the gene ral price level in Japan decreased by 5% from 2000 to 2004. Th e CPI in Japan in 2004 is therefore equal to
a. 100
b. 190
c. 195
d. 205
Use the following diagram to answer the next questions: The diagram shows various possible cons umption bundles under two different budget constraints.
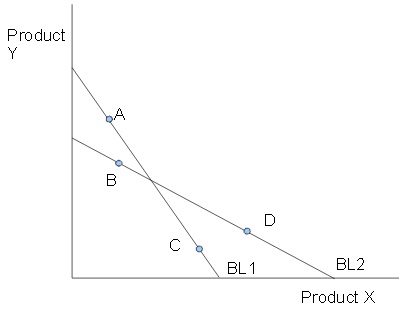
Question 21. Assume the consumer has typical down ward sloping indifference curves. Which combinations of the following points can not be the optimal points with respect to BL1 and BL2?
a. A(with the budget line 1), B(with the budget line 2)
b. A(with the budget line 1), D(with the budget line 2)
c. C(with the budget line 1), B(with the budget line 2)
d. C(with the budget line 1), D(with the budget line 2)
Question 22. What happens to a budget line if simu ltaneously all prices increase by 10% and income increases by 10%?
a. The budget line will remain the same.
b. The budget line will shift out, remain ing parallel to the original budget line.
c. The budget line will shift in, remaining parallel to the or iginal budget line.
d. The budget line will pivot about the in tercept of the axis for the good that the consumer buys more of.
Use the following table to answer the next 2 questions:
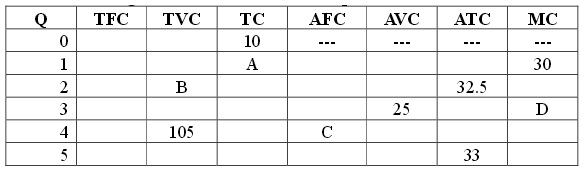
Question 23. Solve for A and B respectively.
a. 40, 55.
b. 40, 65.
c. 20, 65.
d. 10, 55.
Question 24. Solve for C and D respectively.
a. 5/2, 25/2.
b. 5/2, 20.
c. 10, 65/2.
d. 10, 25.
Question 25. A “slightly bowed inward” set of indiffer ence curves represents the two goods as
a. Perfect substitutes.
b. Perfect complements.
c. Very close substitutes.
d. Very close complements.
Question 26. At the equilibrium in the market for bana nas, the price elasticity of demand is 0.4 and the price elasticity of supply is 2. A small price increase due to a shift in the supply curve would lead to _______ in total revenue.
a. an increase
b. a decrease
c. no change
d. an ambiguous change
Use the following information to answer the next 2 questions :
In the perfectly competitive industry for pr inter ink, each firm’s cost functions are. Assume all firms are identical in the market for printer ink. The market demand is P = 40 - (1/2)Q
Question 27. Suppose the industry is in s hort run equilibrium and there are only four firms in the industry competing as perfect competitors. What is the short run equilibrium market price?
a. $4
b. $6
c. $8
d. $10
Question 28. Suppose the industry has entered into long run equilibrium. How many firms will there be in this industry when the industry is in long run equilibrium?
a. 4 firms
b. 5 firms
c. 6 firms
d. 7 firms
Question 29. Suppose the price elasticity of demand for car tires is 0.4, while the income elasticity for car tires is 0.5. Furthermore, suppose a synthetic rubber shortage leads to a 20% increase in the price of tires. Holding everything else constant, what must the increase in income be in pe rcentage terms in order for there to be no change in the quantity demanded in the market for car tires?
a. Income will need to increase by 8%.
b. Income will need to increase by 12%.
c. Income will need to increase by 16%.
d. No increase in income is necessary.
Use the following diagram to answer the next question : '
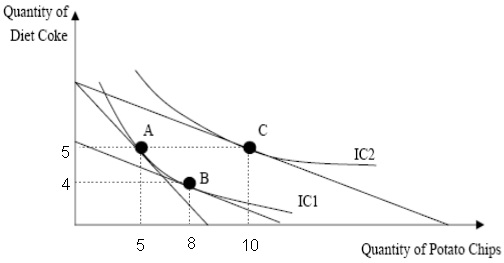
Question 30. Suppose the consumer has faced the price change depicted in the above graph. How much is the substitution effect from that change (hint: measure the substitution effect in terms of the cha nge in the consumption of the good whose price has changed)?
a. 1 unit of diet coke
b. 2 units of potato chips
c. 3 units of potato chips
d. 0 units of diet coke
Question 31. Suppose that every morning Eric buys both soda and coffee. Assume that Eric's indifference curve map consists of normal downward sloping, bowed in toward the origin indifference curves. At his current consumption level, which exhausts all of his income, Eric's marginal utility (MU) from drinking the last can of soda he bought is 25 utils and his marginal util ity from drinking the last cup of coffee he bought is 40 utils. The price of a can of soda is $1, and the price of a cup of coffee is $2. Assume that Eric is a uti lity maximizing individual. Eric should
a. Not change his consumption le vels of soda and coffee.
b. Buy more soda and less coffee.
c. Buy less soda and more coffee.
d. Buy more of both soda and coffee
Use the following information to answer the next 2 questions :
Pierre LaFountaine quits his $25,000 job as a chef to open his own restaurant. At the end of his first year he gave his tax accountant the following information about his restaurant: Wages Paid to Employees $110,000 Rent on Building $5,000 Electricity Bill $10,000 Food Purchases $100,000 Sales Revenue $250,000
Question 32. Pierre’s accounting and economic profits are
a. Both equal to $25,000.
b. $25,000 and zero respectively.
c. $25,000 and $22,500 respectively.
d. $25,000 and -$25,000 respectively.
Question 33. Now suppose Pierre used $50,000 of his saving s that had been earning 5% interest to purchase equipment for his restaurant. What is his tota l economic cost of operating the restaurant?
a. $250,000
b. $275,000
c. $252,500
d. $277,500
Question 34. A sandwich shop is profit maximizing in a perfectly competitive market. In the short run, the market price for the produc t results in the fi rm earning negative economic profit. However, despite this negative economic profit the sandwich shop can reduce its loss by continuing to operate in the short run. At its current level of production the firm's ATC is $4.50 and its AVC is $3.50. Which of the following prices could be the price in this market?
a. $3.00
b. $3.50
c. $4.00
d. $4.50
Question 35. The market for Badger T-Shirts is a perfectly competitive market that is currently in long-run equilibrium. Currently the price of a T-shirt is $10. Due to the disappointing football season, the demand for Badger T-Shirts decreases sharply. In the short run, we expect the price of a T-shirt to ___________ and in the long run, we expect the price of a T-shirt to be ________ assuming everything else is held constant.
a. Fall, less than $10
b. Increase, greater than $10
c. Fall, equal to $10
d. Increase, equal to $10
Use the following graph to answer the next 2 questions :
Question 35. The market for Badger T-Shirts is a perfectly competitive market that is currently in long-run equilibrium. Currently the price of a T-shirt is $10. Due to the disappointing football season, the demand for Badger T-Shirts decreases sharply. In the short run, we expect the price of a T-shirt to ___________ and in the long run, we expect the price of a T-shirt to be ________ assu ming everything else is held constant.
a. Fall, less than $10
b. Increase, greater than $10
c. Fall, equal to $10
d. Increase, equal to $10
Use the following graph to answer the next 2 questions :
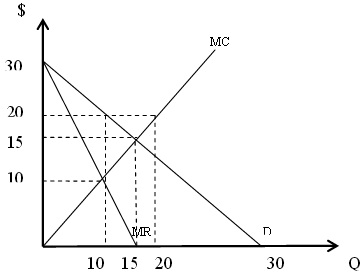
Question 36. The output choice and price level that m aximize this monopolist’s profits are: a. Q=10, P=$20 b. Q=20, P=$20 c. Q=15, P=$15 d. Q=10, P=$10 37. For the above monopolist, what is th e increase in producer surplus this monopolist earns when compared to th is market operati ng as a perfectly competitive industry?
a. $50
b. $75
c. $37.50
d. $25