I. Binary Choice Questions (10 questions)
Problem 1. A vertical demand curve is perfectly________ and a horizontal demand curve is perfectly_________
a. elastic; inelastic
b. inelastic; elastic
Problem 2. Suppose that the CPI in Japan was 200 in 1990 and that the general price level in Japan decreased by 5% from 1990 to 1995. The CPI in Japan in 1995 is therefore equal to
a. 190
b. 195
Problem 3. When the marginal cost curve is ________ the average total cost curve, the average total cost increases as the level of output increases.
a. above
b. below
Problem 4. Perfect Complements only have an income effect since it is not possible to substitute away from one good to the other.
a. True
b. False
Problem 5. Kyle consumes only two goods, x and y. Suppose that each of Kyle's indifference curves is a straight line where each line can be described by the equation U=3x+2y, where (x, y) is a consumption bundle and U is the corresponding level of total utility. The price of x is $6 per unit, and the price of y is $3 per unit. If Kyle wants to maximize his utility, which of the following choices is his best strategy?
a. Kyle should spend all his income on good x.
b. Kyle should spend all his income on good y.
Problem 6. The U.S. imports shoes from China. This means that if the international trade were closed between these two nations, the price of shoes in the U.S. would be ___ the world price of shoes.
a. greater than
b. less than
Problem 7. A firm has just doubled all its inputs and its output has increased by 50%. This firm must be experiencing
a. Diminishing marginal returns
b. Decreasing returns to scale
Problem 8. If the U.S. Government imposes a higher tariff on one good that is currently being imported, the government’s tariff revenue from this good will increase for sure.
a. True
b. False
Use the following information for the next two questions.
The demand for a life-saving drug is perfectly inelastic. The supply curve is upward sloping. Suppose Madison’s government decides to place an excise tax on this drug, and the producer of this drug is legally responsible for paying the tax.
Problem 9. The economic incidence of the tax will fall
a. Solely on the producers.
b. Solely on the consumers.
Problem 10. The deadweight loss due to this tax will be
a. Positive.
b. Zero.
II. Multiple Choice Questions (26 questions)
Use the following information to answer the next three questions:
The government wants to offer a certain amount of funding to the National Institutes of Health. The government plans to finance this funding from an excise tax imposed on tobacco producers. You are told that the market demand curve and market supply curve for tobacco are given by the following equations where Q is measured in pounds of tobacco and P is the price per pound of tobacco.
Market Demand: P = 50 – 2Q
Market Supply: P = 5 + 3Q
Problem 11. Without government intervention, the market equilibrium price and quantity in the market for tobacco is:
a. P = $34, Q = 8 pounds
b. P = $29, Q = 8 pounds
c. P = $32, Q = 9 pounds
d. P = $28, Q = 11 pounds
Problem 12. The government implements an excise tax of $5 for each pound of tobacco sold in the market. What is the value of tax revenue for the government when this tax is implemented?
a. $5
b. $20
c. $40
d. $45
Problem 13. What is the deadweight loss due to the implementation of this excise tax?
a. $1
b. $1.5
c. $2
d. $2.5
Problem 14. Paul and Robin graduated from UW-Madison in the spring of 2007 and have worked in China and India respectively. In 2007, when starting to work, both Paul and Robin made a wage contract to fix their nominal wages for the next three years at the current level. Between 2007 and 2008 the inflation rate of China was positive and was smaller than the inflation rate in India; and between 2008 and 2009, China experienced deflation while India experienced inflation. Paul’s real wage in 2009 is ________ than Paul’s real wage in 2007 and Robin’s real wage in 2009 is _______than Robin’s real wage in 2007.
a. larger; smaller
b. smaller; smaller
c. smaller; larger
d. none of the above answers is correct given the information provided
Use the following information to answer the next four questions.
Consider the butter market. Domestic demand and domestic supply of butter in a small economy is given by the following equations:
Domestic Demand: Q = 8 – 2P
Domestic Supply: Q = 2P
where Q is the quantity of butter measured in pounds and P is the price per pound of butter. The world price of butter is $1 per pound.
Problem 15. Compare the butter market in this small economy when the market is closed to trade and when it is open to trade. Which of the following statements is true?
a. When the economy opens its butter market to trade the quantity demanded domestically of butter increases by 4 units relative to the quantity demanded when the butter market is a closed economy.
b. The surplus of domestic producers decreases by $4 when this economy opens its butter market to trade.
c. The total surplus of the economy increases by $2 when this economy opens its butter market to trade.
d. The domestic price of butter decreases by $2 when this economy opens its butter market to trade.
Problem 16. Suppose this small economy is now open to trade, but the government implements an import quota of 5 units in the market for butter. What is the deadweight loss caused by this import quota?
a. $0
b. $0.125
c. $0.25
d. $0.50
Problem 17. Instead of the import quota of 5 units of butter, suppose that the government implements an import quota of 2 units of butter. What is the deadweight loss caused by this new quota?
a. $0
b. $0.125
c. $0.25
d. $0.50
18. Instead of implementing an import quota, suppose that the government imposes a tariff which creates the same deadweight loss as the quota of 2 units does. What is the tariff?
a. $0.125
b. $0.25
c. $0.50
d. $1.00
Problem 19. Assume that the demand in the market for blueberries is linear and the slope is -2. Suppose that the price elasticity of demand when price equals $8 is 0.5. The price that maximizes total revenue is
a. $10
b. $12
c. $14
d. $16
Use the following table to answer the next two questions:
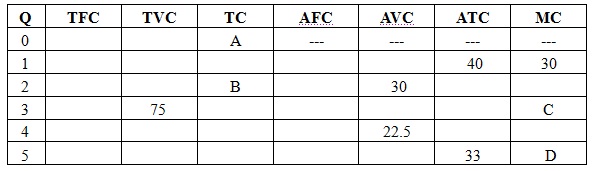
Problem 20. Solve for A and B respectively.
a. 0, 30
b. 0, 60
c. 10, 60
d. 10, 70
Problem 21. Solve for C and D respectively.
a. 10, 25
b. 15, 30.
c. 10, 65.
d. 15, 65.
Problem 22. Which of the following statements is true?
I. The transformation of inputs into output is represented by the firm’s cost function.
II. An input that can be varied in the long run cannot be a fixed input.
III. Marginal product of an input represents the amount of input required to produce an additional unit of output.
a. I and III
b. I
c. II
d. none of the above statements is true
Problem 23. Compared with a closed economy, which of the following occurs as a result of an economy opening its markets to trade and then exporting some units of good X?
a. The domestic consumers of good X gain from this international trade.
b. The domestic producers of good X gain from this international trade.
c. The price paid by the domestic consumers for good X decreases when this economy opens to trade.
d. The quantity supplied of good X by domestic producers decreases when this economy opens to trade.
Use the following information to answer the next three questions.
Suppose you are in charge of the UW-Madison campus parking system. Students’ demand for parking is given by P=200-4Q and Professors’ demand for parking is given by P=100-Q where Q is the quantity of parking permits and P is the price per parking permit. Suppose that the price is initially $40 per parking permit.
Problem 24. What are the price elasticity of students’ demand and the price elasticity of professors’ demand respectively? (Use the point elasticity method to calculate the price elasticity of demand for both types of consumers.)
a. 3/2, 1
b. 1, 3/2
c. 2/3, 1/4
d. 1/4, 2/3
Problem 25. Suppose it is feasible to charge different prices to students and professors for parking permits. If your goal is to maximize revenue from selling parking permits, what is the maximum amount of revenue you can earn through the sales of these parking permits?
a. $2500
b. $3400
c. $5000
d. $6800
Problem 26. Now, your two-tier price system for parking permits is forbidden by university policy and you have to charge a single price for a parking permit whether the customer is a student or a professor. Using the arc elasticity or mid-point method calculate the price elasticity of demand when the price increases from $100 per parking permit to $120 per parking permit.
a. 11/9
b. 12/11
c. 13/12
d. 16/11
Use the following information to answer the next two questions.
Locke is a butcher who produces packaged meats. The following table provides information about Locke’s production function.
Quantity of capital Quantity of labor Total product
(number of knives) (hours of working) (number of packaged meats)
5 0 0
5 10 10
5 20 14
5 30 17
5 40 19
Problem 27. Which of following statements about Locke’s production is true?
a. The variable input in Locke’s production function is the number of knives.
b. The marginal product of capital is increasing.
c. The above table represents Locke’s short-run production function.
d. From the above table we can conclude that Locke’s production function exhibits increasing returns to scale.
Problem 28. Last week Locke purchased 5 new knives and with ten knives, it took him 10 hours to produce 20 packaged meats. Also it turned out that working 20 hours, 30 hours, and 40 hours lead to the production of 28, 34, and 38 units of packaged meats respectively. From this information and the above table we can conclude that Locke’s production function exhibits
a. Increasing returns to scale.
b. Decreasing returns to scale.
c. Constant returns to scale.
d. None of the above answers are correct.
Use the following graph to answer the next four questions.
Bucky spends his income on bagels and cheese. The initial market price of a bagel is $6 per unit, and the initial market price of cheese is $5 per unit. Now suppose the price of a bagel falls to $3 per unit, while Bucky's income and the price of cheese remain the same. The graph below illustrates Bucky's indifference curve map with several budget lines and choices. The dotted straight line passing point C is parallel to the straight line passing through point B.
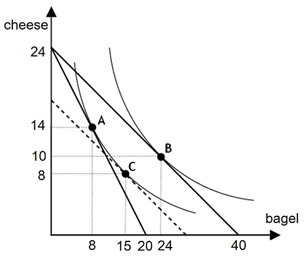
Problem 29. Which of the following statements is true?
a. The change in the price of bagels decreases Bucky's real income.
b. Point C is Bucky's optimal consumption bundle at the initial prices.
c. For Bucky, the consumption bundle A is better than the consumption bundle C.
d. For Bucky, the consumption bundle B is better than the consumption bundle C.
Problem 30. Which of the following statements is true for Bucky given the above graph and the provided information?
a. Both bagels and cheese are inferior goods.
b. Both bagels and cheese are normal goods.
c. Bagels are an inferior good, while cheese is a normal good.
d. Bagels are a normal good and there is not enough information in the graph to tell whether cheese is a normal good or not.
Problem 31. Based on the above graph and the provided information, which of the following changes describes the substitution effect with respect to Bucky’s consumption of bagels?
a. The consumption of bagels increases by 16 units from 8 units to 24 units.
b. The consumption of bagels decreases by 16 units from 24 units to 8 units.
c. The consumption of bagels increases by 9 units from 15 units to 24 units.
d. The consumption of bagels increases by 7 units from 8 units to 15 units.
Problem 32. What is the marginal rate of substitution at point B?
a. 5/12
b. 3/5
c. 5/3
d. 12/5
Use the following table to answer the next two questions.
The following chart shows the marginal product of labor for a small business that has a fixed amount of capital in the short run equal to 10 units of capital. Each unit of capital costs $8 while the wage rate is $5 per worker.
Number of workers MPL
0 -
1 10
2 20
3 20
4 10
5 4
Problem 33. What is the total cost if the firm wants to produce 50 units of output?
a. $15
b. $80
c. $95
d. $100
Problem 34. If each unit of output can be sold for $1, what is the profit maximizing number of units of output this firm should produce in the short run?
a. 10 units of output
b. 50 units of output
c. 60 units of output
d. 64 units of output
Use the following table to answer the next two questions
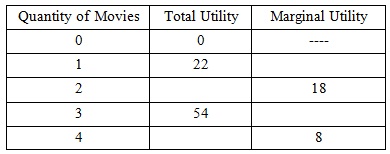
Problem 35. What is the marginal utility of watching the first movie?
a. less than 18
b. 18
c. more than 18
d. None of the above
Problem 36. What is the total utility of watching all four movies?
a. 88
b. 76
c. 62
d. 32