Question 1: Interpret the contents of a given profit and loss account and balance sheet and explaining how accounting ratios can be used to monitor the financial performance of Debenhams.
Profit & Loss Account:
|
|
2007
|
2008
|
|
Sales
|
|
80,000
|
|
120,000
|
|
Less COGS:
|
|
|
|
|
|
Opening Stock
|
25,000
|
|
22,500
|
|
|
Add Purchases
|
50,000
|
|
91,000
|
|
|
Less Closing Stock
|
(15,000)
|
60,000
|
(17,500)
|
96,000
|
|
Gross Profit
|
|
20,000
|
|
24,000
|
|
Less Depreciation
|
1,000
|
|
3,000
|
|
|
Other Expenses
|
9,000
|
10,000
|
6,000
|
9,000
|
|
Net Profit
|
|
10,000
|
|
15,000
|
Balance Sheet:
|
|
2007
|
2008
|
|
Fixed Assets:
|
|
|
|
|
|
Equipment
|
10,000
|
|
20,000
|
|
|
Less Depreciation
|
(8,000)
|
2,000
|
(6,000)
|
14,000
|
|
Current Assets:
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stock
|
15,000
|
|
17,500
|
|
|
Debtors
|
25,000
|
|
20,000
|
|
|
Bank
|
5,000
|
|
2,500
|
|
|
Total
|
45,000
|
|
40,000
|
|
|
Creditors
|
5,000
|
|
(10,000)
|
|
|
Net Assets
|
|
42,000
|
|
44,000
|
|
Financed By:
|
|
|
|
|
|
Capital
|
|
38,000
|
|
36,000
|
|
Add Net Profit
|
|
10,000
|
|
15,000
|
|
Less Drawings
|
|
(6,000)
|
|
(7,000)
|
|
Capital Employed
|
|
42,000
|
|
44,000
|
Interpret the contents of a given profit and loss account and balance sheet and explaining how accounting ratios can be used to monitor the financial performance of Debenhams
|
2007
|
Formulae
|
Workings
|
Answer
|
|
Gross Profit
Margin
|
|
|
|
|
Net
Profit
Margin
|
|
|
|
|
Return On Capital Employed
(ROCE)
|
|
|
|
|
Current Ratio
|
|
|
|
|
Acid
Test
|
|
|
|
|
Debtors
Days
|
|
|
|
|
Creditors
Days
|
|
|
|
Interpret the contents of a given profit and loss account and balance sheet and explaining how accounting ratios can be used to monitor the financial performance of Debenhams
|
2008
|
Formulae
|
Workings
|
Answer
|
|
Gross Profit
Margin
|
|
|
|
|
Net
Profit
Margin
|
|
|
|
|
Return On Capital Employed
(ROCE)
|
|
|
|
|
Current Ratio
|
|
|
|
|
Acid
Test
|
|
|
|
|
Debtors
Days
|
|
|
|
|
Creditors
Days
|
|
|
|
Interpret the contents of a given profit and loss account and balance sheet and explaining how accounting ratios can be used to monitor the financial performance of Debenhams
How do the following ratios help to monitor Debenham's financial performance:
|
Benefit
|
Relate to Figures
|
Impact on Debenhams
|
|
|
2007
|
2008
|
Improved
|
Worsened
|
- Gross Profit
|
|
|
|
|
|
2007
|
2008
|
Improved
|
Worsened
|
- Return on Capital employed (ROCE)
|
|
|
|
|
|
2007
|
2008
|
Improved
|
Worsened
|
- Current Ratio
|
|
|
|
|
|
2007
|
2008
|
Improved
|
Worsened
|
- Debtor Days
|
|
|
|
Question 2: Analyse the reasons why costs need to be controlled to budget
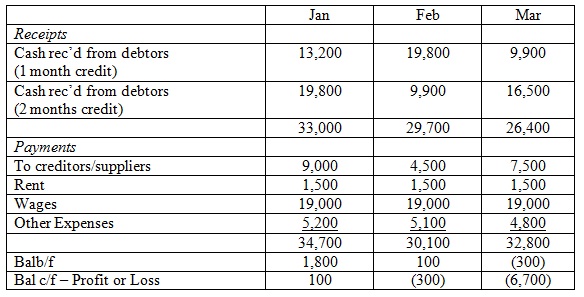
1. From the above information, identify two problems that Debenhams are facing:
2. What would you advise Debenhams to do in order to improve their budget position? (Give two points with explanations).
3. Analyse the reasons why costs need to be controlled to budget
4. The advantages of controlling costs are:
5. The disadvantages of not controlling costs are
6. Potential problems of not controlling costs on the Budgets of Debenhams are:
7. Evaluate the adequacy of accounting ratios
8. Evaluate the problems they have identified from unmonitored costs and budgets
9. Explain three advantages & three disadvantages of budgets:
10. What are the potential problems for Debenhams if budgets are left unmonitored?
11. Evaluate the problems they have identified from unmonitored costs and budgets
12. For Budgets & Costs, provide two recommendations for each to Debenhams on how to improve their position, with explanations:
Question 3: Describe sources of internal & external finance for Debenhams.
1. If Debenhams made £10 million profit in the last financial year, what would they do with this profit?
2. Can you think about another source of finance that Debenhams could potential use?
3. Write a paragraph to answer each of the following:
a. Why may a bank overdraft be more beneficial than a bank loan for Debenhams?
b. Why might investors be more willing to invest into a company, like Debenhams, than save their money in a bank account?
c. Why are shares considered a long-term investment?
d. Why are banks currently very reluctant to lend a small business money?
e. Why may banks be more likely to lend money to a large company, such as Debenhams?
Question 4: Illustrate the use of budgets as a means of exercising financial control of Debenhams
|
|
February
|
March
|
April
|
|
Receipts - Debtors
|
21,000
|
28,000
|
30,000
|
|
Payments:
|
|
|
|
|
Purchases
|
12,000
|
9,000
|
10,000
|
|
Expenses
|
20,000
|
22,000
|
18,000
|
|
Office machinery
|
24,000
|
|
|
|
|
56,000
|
31,000
|
28,000
|
|
Balance B/fwd
|
3,200
|
-31,800
|
-34,800
|
|
Receipts
|
21,000
|
28,000
|
30,000
|
|
|
24,200
|
-3,800
|
-4,800
|
|
Payments
|
56,000
|
31,000
|
28,000
|
|
Balance c/fwd
|
-31,800
|
-34,800
|
-32,800
|
1. From the above budget, identify three problems and for each of your problems, identify a solution:
2. Interpret the contents of a given profit and loss account and balance sheet
a. What does the Trading, Profit & Loss Account show?
b. What does the Gross Profit show?
c. Make a comment about the expenses.
d. What does the Net Profit show?
e. What might Debenhams do with this Net Profit?
f. How do Fixed & Current Assets differ?
g. Why are Current Assets so important?
h. Why is it important to have more Current Assets than Current Liabilities?
i. What does the Net Asset figure show?
j. Why must the last section of the Balance Sheet match the Net Asset figure?
3. Interpret the contents of a given profit and loss account and balance sheet
a. From the trading, profit & loss account, how might Debenhams improve their sales?
b. From the trading, profit & loss account, how might Debenhams reduce their costs?
c. From the balance sheet, how do the current assets cover the current liabilities, in Debenham's day-to-day operations?
d. Why is the balance sheet important to an investor?
4. Illustrate the financial state of Debenhams
What does each of the ratios mean?
- The Gross Profit margin shows .....
- The Net Profit margin shows .....
- The return on capital employed (ROCE) shows .....
- The current ratio shows....
- The acid test ratio shows....
- The debtor days shows....
- The creditor days shows....