Instructions: Below are five problems you should solve all five problems. You may use the discussion board to ask your fellow students questions about their approach to these problems and to discuss necessary information to solve the problems. However please do not post complete solutions. Once you have completed the problems choose the two from problems you are most confident and submit your answers to those problems to the assignment folder. When solving problem 5 be careful and think like a scientist.
Question: The genes for ruby eyes (rb), tan body (t) and cut wings (ct) are all found on the X-chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. All of these are recessive traits. They map in the order rb, ct, t with 12.5 map units between rb and ct and 7.5 map units between ct and t. Suppose you cross a cut wing male with a homozygous female that is both tan and has ruby eyes.
a) What will the F1 females look like?
b) Draw map of the section of the X chromosomes that has these 3 genes for the F1 females
c) Assume you testcross your F1 females.
• What progeny classes would you expect?
• Give approximate numbers for each class based on a total of 2000 progeny.
Assuming i = 1 and there are no double crossovers.
Assuming i = 0 and there are the expected number of double crossovers.
Question: The Neurospora cross was made between a strain that carried mating type A and the mutant allele arg-1(arg) and another strain the carried mating-type a and the wild type arg-1 (+) gene. Four hundred linear octads were isolated and they fell into the 7 categories given in the table below.
a) Label each class and PD, NPD or TT
b) Are the genes linked?
c) What are the map distance between these genes and the centromere?
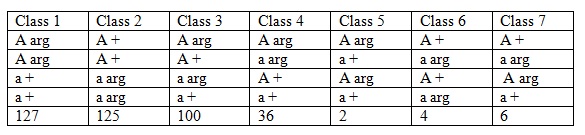
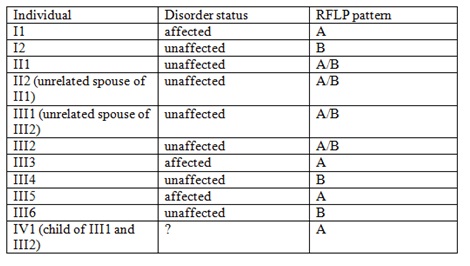
Question: Assume you are analyzing the information from 4 generations of a human family that has an autosomal recessive disorder. You have an RFLP band that is linked to the gene for the disorder. The recombination frequency between the gene and the RFLP is 20%. The data from this family is presented in a table below.
a) What is the probability II1 is a carrier?
b) What is the probability III4 is a carrier?
c) IV2 has not been born yet but amniocentesis has given the banding pattern shown. What is the probability he will have the disorder?
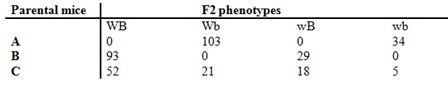
Question: You have four lines of mice that are homozygous at two linked loci. One line has a waltzing gait (W W) and a bent tail (BB) another has normal gait (ww) and a straight tail (bb); the third waltzing gait(WW) and straight tails(bb) and the forth has normal gait (ww) and bent tails (BB). W is dominating to w and B is dominating to b. You cross the pairs of mice and produce an F1 generation. Then you mate the sibs from the F1 generation to each other. What is the chromosomal complement for each of the mice a-c in the table?
Question: Drossophila females of normal appearance but heterozygous for three autosomal genes are mated to males that are homozygous recessive for the three genes: glassy eyes, coal-color bodies and striped thoraxes. 1000 progeny from this cross are scored:
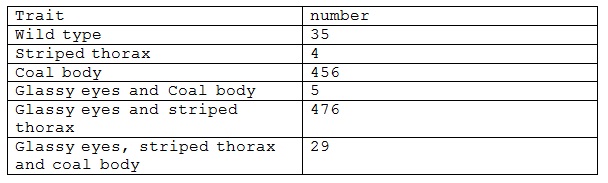
a) Draw the genetic map based on these data
b) Show the arrangement of the genes on the two homologs in the heterozygous female including the distance between the genes in cM.
c) Based on your map what is the expected number of double cross overs?