The temperature reliance of internal energy and enthalpy depends on the heat capacities at constant volume and constant pressure.
The internal energy and enthalpy of chemical systems and the energy changes that accompany chemical reactions depend on the temperature. To make full use of the thermodynamic date we developed, we must see how these data are extended to temperatures other than 25°C.
Heat capacities; it is convenient to deal separately constant pressure processes when the temperature is raised and the energy of the system increases. The heat capacity, already introduced and experimentally determined, as the decrease in the energy of the thermal surroundings that provides the energy to increase the temperature of the system by 1°C, under the specified conditions. Thus we define
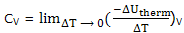
And
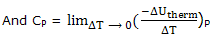
If you think of an actual measurement, you see that to increase the temperature of the system, i.e. for ΔT to be positive, there will be a decrease in the energy of the thermal surroundings, that is, ΔUtherm will be negative. The definitions are then being seen to make heat capacities positive quantities.
Heat capacities at constant pressure CP will be used more than will heat capacities at constant volume CV. Some values for CP are given for a temperature of 25°C. All these values for liquids and solids come from experimental, calorimetric studies that depend on the defining equation. Some of the values for gases are experimental, and others are based on calculations of the type of physical properties.
Heat capacities can be used to extend the 25°C thermodynamic quantities to other temperatures. To do so, we will need heat capacity values over a range of temperatures. An analytical expression, rather than a table of values, is needed for most of the calculations we will do. The two empirical CP versus T expressions that have been most used are
CP = a' + b't + c'T2 + ....
And, CP = a + bT + cT-2 + ...
The second of these two forms is more satisfactory. The coefficients that have been deduced for this equation are given for a few substances.
Heat capacities and internal energies and enthalpies: heat capacities, defined in terms of energy changes in the thermal surroundings, can be expressed in terms energy changes in the system.
If any ordinary chemical process occurs and the system has a constant volume ΔUmech = 0 and ΔU = -ΔUtherm, we can express CV as
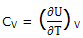
If the system is maintained at a constant pressure, ΔH = - ΔUtherm. We can express CP as
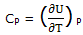
Heat capacities in J K-1 mol-1 at constant pressure (parameters for the equation C°P = (a + bT + cT-2):
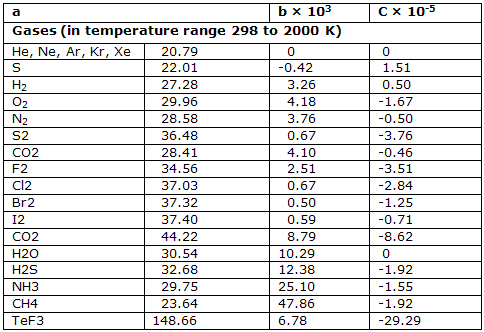
Heat capacities are characteristics of the system. They are directly linked to the way the internal energy and enthalpy change with temperature when the volume or pressure of the system is correctly controlled.