A mechanism for enzyme-catalyzed reactions that leads to the typical rate equation for these reactions can be described.
A variety of rate equations are required to portray the rates of enzymes catalyzed reagents and physical conditions that are encountered. The rate equation of however, is a guide to many of these variations, and the mechanisms of this section, often called the Michaelis-Menten mechanism, is likewise a base for other variations.
The mechanism that accounts for the rate equation is similar to those dealt in with.
With S representing substrate, E the enzyme, and E. S and enzyme substrate complex, the mechanism is presumed to be adequately represented by
E + S 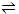 E. S
E. S
E. S 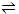 E + products
E + products
The steady state assumption, which, however, is not always clearly applicable in these reactions, leads to
k1[E][S] = k-1[E. S] + k2[E. S]
And [E. S] = k1/k-1 + k2 [E][S]
To bring these expressions to a form that can be compared with the empirical rate equation, we must recognize that only [Etot] = [E] + [E. S], and not [E], is generally known. Often, in fact, only a quantity proportional to [Etot], and not even values of [Etot], is available.
Replacement of [E] in equation by [E] = [Etot] - [E. S] leads to
[E. S] = k1[Etot][S]/(k-1 + k2) + k1[S]
Now this expression for the intermediate E. S can be inserted into the expression for the rate of the net reaction. This rate can be based on the formation of products in the second mechanism step. We have
-d[S]/dt = R = k2[E. S] = k1k2[Etot][S]/k-1 + k2 + k1[S]
= k2[Etot][S]/k-1 + k2)/k1 + [S]
It is customary for the term (k-1 + k2)/k1 to be obtained by the new symbol KM, that is,
KM = k-1 + k2/k1 to give the rate equation result of this mechanism as
R = k2[Etot][S]/KM + [S]
We have come at this stage to the form of the empirical rate equation obtained, we are now in a position to intercept the values of the parameters KM and k2[Etot] in terms of their roles in the roles in the steps of the mechanism.
Reference to equation shows that, as the reaction is proceeding
[E][S]/[E. S] = KM
Thus KM is related to species concentrations, as is the dissociation equilibrium constant for the species [E. S]. the value of KM, however, is given by (k...1 + k2)/k1, and this equal to the value of the dissociation constant for [E. S] only to the extent that k2 is small and can be neglected compared with k...1. Thus when the breakup of the E. S complex to form original E and S species dominates the process whereby the complex forms products, the value of KM approaches the dissociation constant for the E. S complex.
What, now, is the significance of the term k2[Etot]? One first notes that the rate of the overall reaction is
R = k2[E. S]
It follows that k2[Etot] is the rate that the reaction would have if all the enzyme were in the form of the enzyme-substrate complex. Thus k2[Etot] is the maximum rate for a given value of [Etot]. The turnover rate of an enzyme in a particular enzyme-catalyzed reaction is the rate per mole of enzyme, i.e. the turnover rate is equal to the value of k2, and this can be calculated fromk2[Etot] if the total enzyme concentration is known.