Like ammonia, primary, secondary and tertiary amines have a single pair of electrons on N atom. Hence chemical behavior of amines is similar to ammonia. Amines are basic in nature, and in most of the reactions they act as nucleophiles.
1. Reaction with acids
Amines react with aqueous solution of acids to form salts. These reactions hold the fundamental nature of amines.
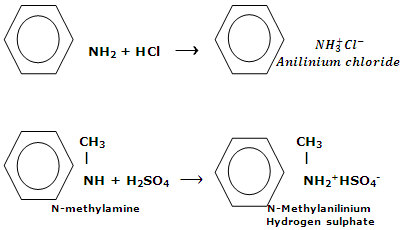
Salts of amine are typical ionic solids. They are non-volatile solids. On heating, these salts decompose before the melting point is reached. Amine salts are soluble in water while unsolvable in non-polar solvents. A water insoluble amine can be separated from non-basic compounds by its solubility in aqueous solutions of acids. From the aqueous solution, the amine can be regenerated by making it alkaline.
2. Reaction with metal ions
Lower aliphatic amines form coordination complexes with metal ions like Ag+ and Cu2+. For example, silver chloride dissolves in aqueous solution of ethylamine and copper sulphate forms a deep blue solution.
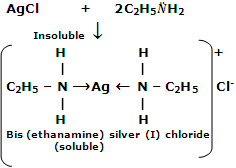
3. Reaction with alkyl halides (Alkylation)
Amines react with alkyl halides to form amines of higher class. In this reaction, the amine acts as nucleophile bringing about nucleophilic substitution of alkyl halide.
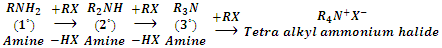
Since in this reaction hydrogen atoms attached to nitrogen in amines is referred to as alkylation of amines.
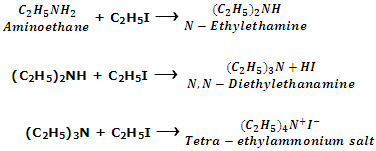
Aromatic amines also undergo similar reaction. For example, when aniline is treated with excess of methyl iodide under pressure, mixture of secondary, tertiary amines and quaternary salt are formed.