In these reaction oxygen atom of carbonyl group is replaced by either one divalent group or two monovalent groups.
Reaction by ammonia derivatives: aldehydes and ketones react with a number of ammonia derivatives such as hydroxylaminem hydrazine, semicarbazide etc. in weak acidic medium. In general, if we represent these derivatives by H2N-G, then their reaction with aldehydes and ketones can be represented as follows:
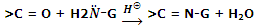
These derivatives are crystalline solids and having sharp melting and boiling points. Thus, they are used for the identification of carbonyl compounds. The various ammonia derivatives and their reaction products with carbonyl compounds are summarized in the same way.
The reactions of some aldehydes and ketones with ammonia derivatives are given below:
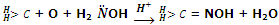
Reaction by hydroxylamine: aldehydes and ketones react with hydroxylamine to give oximes.
The oximes can be hydrolysed back to aldehydes and ketones by reaction with acids. These can also be reduced to amines by reaction with Na, Mg, etc.
Reaction by hydrazine: aldehydes and ketones react with hydrazine to give hydrazones.
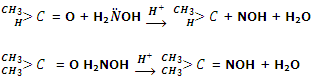
Reaction by phenylhydrazine: aldehydes and ketones react with phenylhydrazine to give phenylhydrazones.
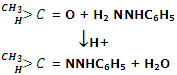
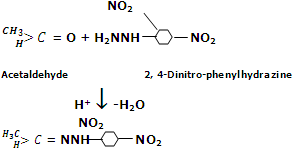
Reaction by 2, 4-Dinitrophenyl-hydrazine: aldehydes and ketones react with dinitro-phenylhydrazine to form 2, 4 dinitrophenyl-hydrazones commonly known as DNP or Brady's reagent.