The bonding in ionic molecules can be described with a coulombic attractive term.
For some diatomic molecules we take quite a different approach from that used in preceding sections to describe the bonding. Ionic bonds are interpreted in terms of the coulombic attraction between ions. Since the electronic details of these ions are not dealt with the approach does not require quantum mechanical calculations. The treatment is easier but, as you will see, less satisfying than those in which a complete quantum mechanical description is set up and, with various recognized simplifications, solved.
Let us consider, to be specific, the NaCl molecule. The molecule exists in the high temperature vapour, and its bonding energy and equilibrium bond length and some features of its energy versus internuclear distance curve are known. These are shown by the solid curve of the products of dissociation of an NaCl molecule are the gas phase Na and Cl atoms.
Now let us attempt to develop an energy intermolecular distance curve by using the internuclear model. The energy required converting Na atoms to Na+ ions and Cl atoms to Cl- ions, all in the gas state, can be calculated from ionization:
Na 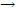 Na = + e- ?U = =495 kJ mol-1
Na = + e- ?U = =495 kJ mol-1
Cl + e- 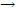 Cl- ?U = - 349 KJ mol-1
Cl- ?U = - 349 KJ mol-1
And thus,
Na = Cl 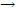 Na+ + Cl- ?U = + 146 KJ mol-1
Na+ + Cl- ?U = + 146 KJ mol-1
Infinitely separated gas phase Na and Cl ions lie at an energy 147 KJ mol-1 higher than separateNa and Cl atoms.
As Na+ and Cl- ions approach each other, the potential energy becomes more negative. If we treat the ions at point charges, this potential energy is given by the coulombic term:
Ucoul = - e2/ (4∏e0)/ r
Where r is the internuclear distance, a curve for this function, based on the energies of separateNa+ and Cl- ions has been added.
An opposing effect exists in the form of repulsion between the nuclei, each with its closed shell of electrons. This repulsion term cannot easily be deduced, and it is satisfactory here to use an empirical expression to represent the repulsion that sets in at small internuclear distances. The variation of this repulsive energy contribution with internuclear distance is satisfactorily represented by an empirical equation of the form:
Urep = be-r/p, where p and b are empirical constants.
Furthermore, to a quite good approximation, the constant p can be taken to be the same for all ionic molecules and equal to 0.30 × 10 -10 m = 30 pm. Thus,
Urep = be -r/(0.30 × 10-10)
The total potential energy can now be written as:
U = - e2/(4∏e0)/r + be -r/(0.30 × 10-10)
The value of the remaining empirical constant b can be deduced by requiring U to have a minimum at the experimentally determined equilibrium bond length. Setting the derivate equal to zero for r = 2.36 × 10-10 m, the equilibrium bond length for NaCl, gives b = 1.95 × 105 kJmol-1. Substitution of the numerical value e2/(4∏eo) and expressing r in picometers gives:
U(kJ mol-1) = - 138,900/r + 195,000e-r/30 (r in picometers)
Calculated dissociation energy = 514 - 146 = 368 KJ mol-1
The result can be compared with the experiment value of 406 kJ mol-1
The attraction energy curve, the repulsion energy curve, and the total energy curve are the ionic model describes the system satisfactorily up to an internuclear separation of about 100 pm. Then the bond description must changes so that at complete separation the products released from each other are atoms rather than ions.