Area Functions
1. (a) Draw the line y = 2t + 1 and use geometry to find the area under this line, above the t - axis, and between the vertical lines t = 1 and t = 3.
(b) If x > 1, let A(x) be the area of the region that lies under the line y = 2t + 1 between t = 1 and t = x. Sketch this region and use geometry to find an expression for A(x).
(c) Differentiate the area function A(x). What do you notice?
2. (a) If 0 < x < π, let
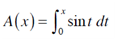
where A(x) represents the area of a region. Sketch the region.
(b) Use the Evaluation Theorem to find an expression for A(x).
(c) Find A'(x). What do you notice?
(d) If x is any number between 0 and π, and h is a small positive number, then A(x + h) - A(x) represents the area of a region. Describe and sketch the region.
(e) Draw a rectangle that approximates the region in part (d). By comparing the areas of these two regions, show that
A(x + h) ! A(x)/h ≈ sin x
(f) Use part (e) to give an intuitive explanation for the result of part (c).
3. (a) Draw the graph of the function f (x) = cos(x2) in the viewing rectangle [0, 2] by [-1.25, 1.25].
(b) If we define a new function g by
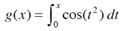
then g(x) is the area under the graph of f from 0 to x [until f(x) becomes negative, at which point g(x) becomes a difference of areas]. Use part (a) to determine the value of x a t which g(x) starts to decrease. [Unlike the integral in Problem 2, it is impossible to evaluate the integral defining g to obtain an explicit expression for g(x).]
(c) Use the integration command on your calculator or computer to estimate g(0.2), g(0.6), ..., g(1.8), g(2). Then use these values to sketch a graph of g.
(d) Use your graph of g from part (c) to sketch the graph of g' using the interpretation of g'(x) as the slope of a tangent line. How does the graph of g' compare with the graph of f?
4. Suppose f is a continuous function on the interval [a, b] and we define a new function g by the equation
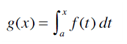
Based on your results in Problems 1-3, conjecture an expression for g'(x).