Assignment 1:
Q1. Is it possible for the unemployment rate to rise at the same time that the number of people working increases?
a. no
b. yes, if labor force growth outpaces growth in the number of people working
c. yes, if the new workers are employed less than full time
d. yes, if established workers keep their jobs but no longer have the option of working overtime
Q2. During the Great Depression,
a. the U.S. unemployment rate reached its historical maximum.
b. most people who couldn't find work left the labor force, so the official unemployment rate remained low.
c. unemployment statistics were not collected.
d. the unemployment rate was not unusually high, but wage levels were low.
Q3. COLA's are designed to
a. improve worker productivity.
b. reduce the inflation rate.
c. protect against unanticipated inflation.
d. protect workers against layoffs.
Q4. Mrs. Smith lost her job at a textile mill due to competition from cheaper imported goods. She would be classified as
a. frictionally unemployed.
b. structurally unemployed.
c. not in the labor force.
d. cyclically unemployed.
Q5. Unanticipated inflation benefits
a. people or businesses who owe money.
b. people who live on fixed nominal incomes.
c. people or businesses who lend money.
d. people with savings.
Q6. The Consumer Price Index
a. measures price changes in all goods, not just a market basket of select items.
b. allows for the change in purchasing patterns that result from changes in
b. allows for the change in purchasing patterns that result from changes in relative prices.
c. is a fixed quantity price index.
d. measures the rate of anticipated inflation.
Q7. When the economy is experiencing a contraction, there is an increase in
a. frictional unemployment.
b. seasonal unemployment.
c. cyclical unemployment.
d. structural unemployment.
Q8. Table:
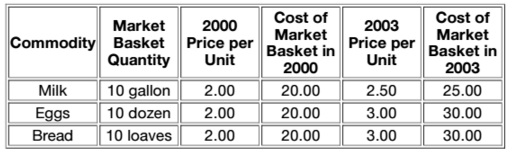
In Table above the total cost of the market basket in 2003 was
a. $8.50.
b. $60.00.
c. $6.00.
d. $85.00.
Q9. The unemployment rate tends to decrease in periods of business expansion.
a. true
b. false
Q10. Structural unemployment is the result of
a. workers not having the right information about job prospects.
b. the inability of some firms to smooth out the available work from season to season.
c. workers not having the right skills.
d. government mandates that cause employers to reduce their demand for labor.
Q11. Which of the following statements is correct?
a. An economy can go through contractions and expansions while still growing over time.
b. The depth and the length of all business downturns are identical.
c. Business cycles are caused by seasonal unemployment changes.
d. Business fluctuations are caused by unanticipated inflation.
Q12. Unemployment statistics are often criticized
a. for overstating the number of people out of work, as it includes all low-income workers.
b. for overstating the number of people out of work, as retirees are included in the statistics.
c. for understating the number people out of work, as full-time college students are excluded.
d. for understating the number of people out of work, as discouraged workers are excluded.
Q13. The downward slope of the aggregate demand curve shows that
a. there can never be an equilibrium between aggregate supply and aggregate demand.
b. a higher price level will cause real output demanded to be higher.
c. a lower price level will cause real output demanded to be higher.
d. an increase in aggregate demand reduces aggregate supply.
Q14. The upward slope of the supply curve is explained by
a. the open economy effect.
b. the profit motive of firms.
c. the real balance effect.
d. the bargaining strength of labor unions.
Q15. Aggregate demand is
a. the horizontal summation of all demand curves for state, local, and federal governments and business firms.
b. the total quantity of all goods sold in an economy in a year.
c. the sum of all planned expenditures for the economy.
d. the horizontal summation of all demand curves for a product.
Q16. Households receive money income from selling factor services to businesses.
a. true
b. false
Q17. Aggregate supply is
a. the summation of all product supply curves.
b. the horizontal summation of all supply curves for services.
c. the sum of all planned production in the economy.
d. the stock of all goods in the economy.
Q18. What is measured on the horizontal axis when we draw a graph of aggregate supply?
a. the price level
b. real GDP
c. output of consumer goods
d. output of capital goods
Q19. An increase in aggregate demand is shown by
a. a rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve.
b. a movement up along the aggregate demand curve.
c. a movement down along an aggregate demand curve.
d. a leftward shift in the aggregate demand curve.
Q20. A shift in aggregate demand will change the equilibrium price level.
a. true
b. false
Q21. The intersection of aggregate supply and aggregate demand determines the equilibrium price level and equilibrium real output.
a. true
b. false
Q22. What determines the total value of annual U.S. GDP?
a. the Federal Reserve Board
b. the Congressional Budget Office
c. the spending decisions of consumers, firms, and governments
d. Wall Street
Q23. If the amount of goods supplied by firms exceed planned spending then
a. inventories accumulate and firms reduce prices.
b. inventories accumulate and firms raise prices.
c. inventories are depleted and firms raise prices.
d. inventories are depleted and firms reduce prices.
Q24. The real-balance effect indicates that a higher price level causes
a. the real value of financial assets to increase.
b. the real value of financial assets to decrease.
c. consumers to save more.
d. banks to be more restrictive in their lending practices.
Q25. Aggregate supply is the total of all planned production for an economy over a specific time period.
a. true
b. false
Q26. Contractionary fiscal policy is used when the economy is overheated.
a. true
b. false
Q27. Investment is
a. goods bought by households.
b. the production of goods for immediate satisfaction.
c. spending by businesses on equipment which can be used to produce goods and services in the future.
d. the purchase of stocks and mutual funds.
Q28. Increases in the marginal propensity to consume will
a. shift the aggregate supply curve to the right.
b. shift the aggregate supply curve to the left.
c. increase the multiplier.
d. increase the marginal propensity to save.
Q29. If the marginal propensity to consume is .9 and there is a $3 billion increase in planned investment, national income will increase by
a. $3.0 billion.
b. $30.0 billion.
c. $6.0 billion.
d. $2.7 billion.
Q30. Changes in investment spending
a. do not affect the equilibrium level of real output.
b. have a multiplier effect.
c. do not affect aggregate demand.
d. affect aggregate supply, but not aggregate demand.
Q31. When business inventories accumulate beyond what firms had planned, the economy returns to equilibrium as the price level falls.
a. true
b. false
Q32. Contractionary fiscal policy is used when
a. the goal is to increase aggregate demand.
b. the goal is to reduce unemployment.
c. the economy is overheated.
d. the goal is to increase aggregate supply.
Q33. The intent of discretionary fiscal policy is to smooth out fluctuations in business activity by shifting the aggregate supply curve.
a. true
b. false
b. false
Q34. If a $12,000 increase in income boosts consumption spending by $8,400, then the marginal propensity to consume is
a. .50.
b. .70.
c. .80.
d. .60.
Q35. Discretionary fiscal policy involves changes in government spending and taxation in order to offset fluctuations in the level of business activity.
a. true
b. false
Q36. If your income goes up by $1,000 per week, and your consumption goes up by $800 per week, you have a marginal propensity to consume of
a. 0.2.
b. 1.0.
c. 1.2.
d. 0.8.
Q37. Equilibrium in the macroeconomy occurs when
a. total planned expenditures equal real national income.
b. total planned consumption expenditures equal real national income.
c. net exports equal inventory changes.
d. planned investment spending equals net exports of zero.
Q38. An increase in the marginal propensity to save
a. increases the value of the multiplier.
b. decreases the value of the multiplier.
c. increases the crowding out effect.
d. increases the marginal propensity to consume.
Q39. Which of the following assets are counted in M2?
a. real estate
b. credit card accounts
c. mutual market mutual funds
d. gold
Q40. Credit card balances are included in M1.
a. true
b. false
Q41. When defining money as M1, you are looking at those assets that
a. earn interest.
a. earn interest.
b. can be used in transactions.
c. serve as a medium of exchange but are not liquid.
d. are liquid but do not serve as a medium of exchange.
Q42. The existence of money in an economy promotes efficiency by
a. facilitating trade, thereby allowing for greater specialization.
b. creating an equal distribution of income.
c. allowing for the formation of corporations as legal entities.
d. creating incentives to be self-sufficient.
Q43. The direct exchange of one good or service for another is called
a. barter.
b. a standard of deferred payment.
c. extortion.
d. a token exchange.
Q44. The assets included in M1 are
a. the money that has been created outside the banking system.
b. readily used to conduct marketplace transactions.
c. assets of value that do not serve as a medium of exchange.
d. not liquid.
Q45. Which of the following is TRUE?
a. M1 includes those assets that are near moneys.
b. M1 includes those assets held for the purpose of engaging in marketplace transactions.
c. M2 is equal to the value of GDP.
d. M1 is always larger than M2.
Q46. Cigarettes served as money in some prisoner of war camps during World War II. Given this, we would have observed that
a. only government-issued cigarettes were accepted as money.
b. people resorted to barter rather than use cigarettes as money.
c. no one ever smoked a cigarette in the camps.
d. prices of other goods were expressed in terms of cigarettes.
Q47. Why is a smart card less vulnerable to theft than is currency?
a. because a smart card cannot be used without a photo ID of the card holder
b. because a smart card cannot be used without a fingerprint of the card holder
c. because a smart card cannot be used without online authorization from the cardholder's bank
d. because a smart card cannot be used without a personal code
Q48. To the extent that banks hold excess reserves, the actual expansion of the money supply will be greater than that predicted by the size of the money multiplier.
a. true
b. false
Q49. The Federal Reserve System
a. regulates the U.S. fiscal policy.
b. serves as the U.S. central bank.
c. consists of 8 Federal Reserve districts.
d. does not have any control over the money supply.
Q50. Which one the following is TRUE?
a. The Federal Reserve regulates the money supply by changing the level of reserves in the banking system.
b. The money supply is independent of Federal Reserve actions.
c. The money multiplier is determined by the current interest rate.
d. The Federal Reserve regulates the money supply by determining the number of banks that will be allowed to issue loans in any one year.
Assignment 2:
Q1. Keynesian economists believe that monetary policy works through its effect on
a. long-run aggregate supply.
b. the interest rate.
c. consumer confidence.
d. the federal budget deficit.
Q2. A contractionary monetary policy
a. will lead to an increase in aggregate demand.
b. will lead to a decrease in aggregate demand.
c. is brought about by a lowering of the required reserve ratio.
d. is brought about by lower interest rates.
Q3. The Federal Reserve increased the money supply significantly during the Great Depression, but prices continued to fall anyway.
a. true
b. false
Q4. The effect of contractionary monetary policy is to
a. decrease real output and increase the price level.
b. increase real output and decrease the price level.
c. increase real output and increase the price level.
d. decrease real output and decrease the price level.
Q5. A central bank that engages in inflation targeting is following a monetary rule.
a. true
b. false
Q6. Both Keynesians and monetarists agree that monetary policy works by shifting aggregate supply.
a. true
b. false
Q7. Keynesian theory argues that
a. decreases in the money supply lead to increases in the interest rate which increases investment which increases the level of real GDP.
b. increases in the money supply lead to decreases in the interest rate which increases investment which increases the level of real GDP.
c. increases in the money supply lead to decreases in the interest rate which decreases investment which decreases the level of real GDP.
d. increases in the money supply cause consumers to spend more which reduces the unemployment rate and therefore increases real GDP.
Q8. With an expansionary monetary policy, the Federal Reserve creates a business environment in which the supply of credit increases.
a. true
b. false
Q9. There appears to be no long-term link between increases in the money supply and rates of inflation.
a. true
b. false
Q10. The goal of contractionary monetary policy is
a. to counteract the impact of fiscal policy.
b. to fight inflation.
c. to reduce the price of basic resources.
d. to fight a recession.
Q11. The effect of expansionary monetary policy is to
a. increase real output and decrease the price level.
b. decrease real output and increase the price level.
c. increase real output and increase the price level.
d. decrease real output and decrease the price level.
Q12. An expansionary monetary policy results in lower interest rates, which in turn
a. lead to higher rates of taxation.
b. cause firms to invest more.
c. lead to lower bond prices.
d. cause consumers to save more.
Q13. Labor productivity is defined as
a. the amount of input per worker.
b. the increase in output per unit of machinery.
c. the amount of output per worker.
d. the amount of workers per unit of input.
Q14. Economic growth is reflected in
a. growth in total output.
b. an increase in tax revenue.
c. increases in the level of employment.
d. increase in per capita real GDP.
Q15. A small reduction in a country's growth rate is a concern to policymakers because
a. this leads to deflation, which makes people feel worse off.
b. a reduction usually leads to future reductions until finally the economy stagnates.
c. policymakers focus too much on economic growth and not enough on increasing savings rates.
d. a small change can have large effects on per capita GDP over time.
Q16. Economic growth is reflected in the production possibilities curve becoming flatter.
a. true
b. false
Q17. Secondary schooling makes measurable contributions to economic growth in developing countries.
a. true
b. false
Q18. Which of the following is the most important factor affecting economic growth?
a. the rate of interest
b. the exchange rate
c. the price level
d. the rate of saving
Q19. Which one of the following is FALSE?
a. Increases in the capital stock can improve the productivity of labor.
b. Increases in the size of the labor force improve labor productivity.
c. Increases in labor productivity can enhance economic growth.
d. Labor productivity contributes to economic growth.
Q20. Which one of the following is TRUE?
a. Small changes in the annual growth rate amount to a measurable difference in the long-term growth trend of a country.
b. For every country that experiences an increase in its growth rate, there must be another experiencing a decline.
c. A well-defined system of property rights benefits only the wealthy, and consequently it produces income inequality that will stifle economic growth.
d. Restricting imports will enhance a country's economic growth.
Q21. Economic growth can also be defined as the cumulative contribution of the rate of growth of capital, the rate of growth of labor, and the rates of growth of capital and labor productivity.
a. true
b. false
Q22. Research has shown that the growth of developing countries is most strongly enhanced by
a. providing a good secondary education.
b. increasing the money supply.
c. providing incentives to have large families.
d. providing colleges and universities.
Q23. The more certain property rights are, the more capital accumulation there will be, and therefore the greater economic growth.
a. true
b. false
Q24. A small increase in the annual rate of economic growth can lead to a larger increase in growth over time due to the effects of
a. regression towards the mean.
b. compounding.
c. averaging.
d. the money supply.
Q25. Table:
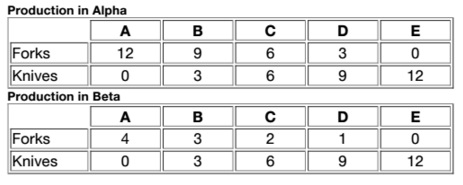
Table shows the quantities of forks and knives that can be produced with the full amount of resources in each of two countries, Alpha and Beta.
Refer to Table. If these two countries specialize based on comparative advantage, then
a. Alpha should specialize in forks and Beta should specialize in knives.
b. Beta should produce both items.
c. Alpha should specialize in knives and Beta should specialize in forks.
d. Alpha should specialize in producing both items.
Q26. Which of the following is a true statement?
a. Exporters benefit from trade and importers do not.
b. Free trade harms domestic producers of goods that face import competition.
c. Consumers benefit from trade and producers do not.
d. Everyone benefits from free trade in the short run.
Q27. Protection should be withdrawn from an infant-industry when the companies in the industry
a. reach a sufficient size to compete with foreign firms.
b. become profitable.
c. are listed on the domestic stock exchange.
d. double their sales revenues.
Q28. Table:
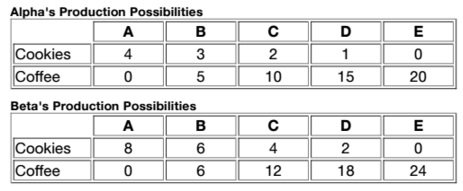
Table shows the quantities of cookies and coffee that can be produced with the full amount of resources available in each of two countries, Alpha and Beta.
Using the information in Table, which statement is TRUE?
a. Beta has the lower opportunity cost of producing cookies.
b. Alpha has the lower opportunity cost of producing both coffee and cookies.
c. Alpha has the lower opportunity cost of producing cookies.
d. Both countries have the same opportunity cost of producing cookies.
Q29. The law that created the high level of tariffs in United States in the 1930s is
a. the World Trade Act.
b. the North American Free Trade Agreement.
c. the Smoot-Hawley Act.
d. the Compromise Tariff.
Q30. If there are two goods and two countries, then one country can have
a. an absolute advantage in both goods but a comparative advantage in only one good.
b. an absolute advantage in both goods and a comparative advantage in both goods.
c. an absolute advantage in neither good and a comparative advantage in both goods.
d. an absolute advantage in one good, an absolute disadvantage in the other good, and a comparative advantage in neither.
Q31. Countries engaged in international trade specialize in production based on
a. the differences in transportation costs.
b. comparative advantage.
c. relative price levels.
d. relative foreign exchange rates.
Q32. Trade restrictions tend to make domestic products
a. cheaper because they do have to compete with foreign goods.
b. cheaper because they do not have to compete with foreign goods.
c. more expensive because they do not have to compete with foreign goods.
d. more expensive because they have to compete with foreign goods.
Q33. A basic proposition in international trade is that
a. trade is determined by absolute advantage.
b. in the long run, imports are paid for by exports.
c. fair trade is more important than free trade.
d. everyone is made better off by free trade.
Q34. The European Union is an example of a common market.
a. true
b. false
Q35. In the United States today, imports are over
a. 22 percent of GDP.
b. 26 percent of GDP.
c. 14 percent of GDP.
d. 18 percent of GDP.
Q36. Table:
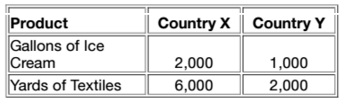
Table shows the combinations of quantities of two goods, gallons of ice cream and yards of textiles, that can be produced with all of the resources available in two countries, X and Y. Refer to Table above. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
a. Country X has a lower opportunity cost of producing ice cream than does Country Y.
b. Country Y has a comparative advantage in producing textiles.
c. Country X has a comparative advantage in producing ice cream.
d. In Country X, the opportunity cost of producing a gallon of ice cream is three yards of textiles.
Q37. If the infant-industry argument is used to protect an industry that has already matured then
a. consumers lose because they pay a price for a product which is below the world price.
b. consumers lose because they pay a price for a product which is above the world price.
c. no one loses.
d. stockholders lose because the firm cannot compete with other firms.
Q38. The growth in world trade since the 1950s has been much less than the growth in world GDP.
a. true
b. false
Q39. The fact that the United States has a trade deficit means that
a. U.S. workers cannot compete with workers overseas.
b. the United States has a surplus in its capital account.
c. interest rates in the United States are low compared to the world average.
d. the United States has a deficit in its capital account.
Q40. A financial strategy that reduces the chance of suffering losses arising from foreign exchange risk is referred to as
a. hedging.
b. conversion depletion.
c. foreign exchange leverage.
d. transaction mitigation.
Q41. If the capital account is in surplus, the current account will be in deficit.
a. true
b. false
Q42. The balance of payments is equivalent to the balance of trade.
a. true
b. false
Q43. Floating exchange rates are determined by
a. the predictions of currency speculators.
b. the government of the importing country.
c. the forces of supply and demand.
d. the government of the exporting country.
Q44. An increase in the U.S. demand for Japanese yen causes
a. an increase in the dollar-price of yen.
b. an increase in the demand for U.S. goods.
c. an increase in the yen-price of dollars.
d. a decrease in the supply of yen.
Q45. When a country intervenes in foreign currency markets to maintain a fixed exchange rate
a. it is engaged in hedging.
b. it increases the foreign exchange risk faced by its citizens.
c. it does so by using its foreign exchange reserves.
d. it smoothes out fluctuations in the level of business activity.
Q46. Assume that there is an increased demand in the United States for Australian wines. If all other factors are held constant, this will result in
a. an appreciation of the Australian dollar.
b. a movement along the demand curve for Australian wine.
c. a decrease in the supply of U.S. dollars in the foreign exchange market.
d. an appreciation of the U.S. dollar.
Q47. The possibility that changes in the value of a nation's currency will result in variations in the market value of a businesses assets is referred to as
a. hedge risk.
b. conversion risk.
c. foreign exchange risk.
d. transaction risk.
Q48. The balance of payments consists of the
a. capital account, official reserve transactions account, and recent account.
b. current account, official reserve transactions account, and monetary account.
c. current account, capital account, and official reserve transactions account.
d. current account, capital account, and gold flows.
Q49.
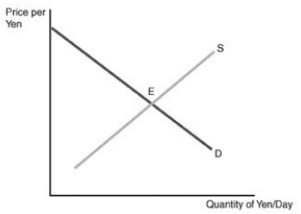
Figure: Foreign Exchange Market for Yen
Refer to Figure Suppose E is the original equilibrium. An increase in the inflation rate in Japan relative to the rate in the United States generates
a. an increase in the price of yen and an increase in the quantity of yen sold per week.
b. a decrease in the price of yen and a decrease in the quantity of yen sold per week.
c. a decrease in the price of yen and an increase in the quantity of yen sold per week.
d. an increase in the price of yen and a decrease in the quantity of yen sold per week.
Q50. Every transaction concerning the exportation of goods from America constitutes a
a. demand for foreign currencies and a supply of dollars.
b. demand for dollars with no effect on markets for foreign currencies.
c. supply of foreign currency with no effect on the market for the dollar.
d. supply of foreign currencies and a demand for dollars.