Solve the following problem:
Five variables for 96 nations in the world.
Onlinepop- Online Population
PC's - Number of Personal Computeres
Phones - Number of landline phones
Educ- Percent of GNP spent on education
GNPPC -Gross National Product per capita
Here is correlation matrix on data set:
|
|
Onlinepop
|
PCs
|
Phones
|
Educ
|
GNPPC
|
|
Onlinepop
|
1
|
|
|
|
|
|
PCs
|
0.990643
|
1
|
|
|
|
|
Phones
|
0.319927
|
0.275276
|
1
|
|
|
|
Educ
|
0.049997
|
0.049423
|
0.369801
|
1
|
|
|
GNPPC
|
0.509078
|
0.477851
|
0.874735
|
0.318304
|
1
|
Assigment was to Regress Onlinepop against PC's, Phones, and Educ and then to regress the predicted values of the dependent variable Onlinepop against the residuals resulting in the following scatterplot in order to detect for heteroskedasticity.
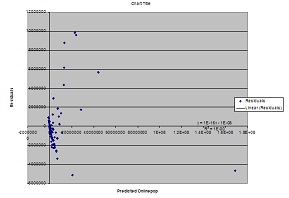
Next based on results of model I was to consider three scenarios. First, triple Education expenditure. Second, double PC's. Third, double Phones. Here are results of model. R square was .98
Coefficients Standard Error T stat P-value
Intercept 544579.306 613179.8725 0.89 .38
PCs 0.937418021 0.013151766 71.28 2.67337E-82
Phones 0.218685792 0.054724064 3.99 .0001
Educ -187381.0927 132987.9076 -1.40 .1622
QUESTION - I don't understand why variable Educ has a negative coefficient. Intutitively, I would expect a positive sign. Can you explain why? Could it be multilcollinearity or is it the heteroskedasticity at work?