Assignment:
1) What is necessary for an economic downturn to be classified as a recession?
A) The unemployment rate reaches 10 percent
B) Negative inflation for one year
C) Negative economic growth for one year
D) Aggregate economic output falls for two consecutive quarters
The following table contains statistics for the country of Caddyville in 2013.
|
Population
|
140,000
|
|
Children under 18
|
28,000
|
|
Students in Secondary education
|
7,000
|
|
Age 65 and over
|
24,000
|
|
Not looking for work
|
14,000
|
|
Unemployed
|
4,800
|
|
GDP (national income)
|
$10 billion
|
2) Refer to the table above. What is Caddyville's per capita income for 2013?
A) $52,935
B) $61,067
C) $71,429
D) $87,532
3) Refer to the table above. What is the size of the labor force in Caddyville for 2013?
A) 62,200
B) 67,000
C) 74,000
D) 88,000
4) Refer to the table above. What is the unemployment rate in Caddyville for 2013?
A) 5.5 percent
B) 6.5 percent
C) 7.2 percent
D) 7.7 percent
The following table contains statistics for the country of Gregorville in 2017, a country in which all must either attend school, be available for work, or be retired.
|
Population
|
140,000
|
|
Students
|
28,000
|
|
Retirees
|
36,000
|
|
Employed
|
62,000
|
|
Jobless
|
14,000
|
|
Jobless and actively looked for work in the prior 4 weeks
|
10,000
|
5) Refer to the table above. What is the labor force?
A) 72,000
B) 62,000
C) 76,000
D) Not enough information provided
6) Refer to the table above. What is the labor force participation rate?
A) 51.4 percent
B) 44.3 percent
C) 54.3 percent
D) Not enough information provided
7) Refer to the table above. What is the unemployment rate?
A) 13.9 percent
B) 19.4 percent
C) 33.3 percent
D) 108.3 percent
8) Refer to the table above. What is the labor force participation if 5,000 of those actively looking for a job find one?
A) 51.4 percent
B) 44.3 percent
C) 54.3 percent
D) Not enough information provided
9) Refer to the table above. What is the unemployment rate if 5,000 of those actively looking for a job find one?
A) 6.9 percent
B) 13.9 percent
C) 19.4 percent
D) 86.1 percent
10) GDP is a measure of ________, not a measure of ________.
A) sales to consumers; production
B) production; sales to consumers
C) sales to consumers; consumption
D) income; production
11) Double counting occurs when ________ included in the calculation of the GDP.
A) inputs are
B) unsold inventories are
C) depreciation is
D) household production is
12) Which of the following is likely to be included in a country's GDP for a particular year?
A) The total amount of steel used in the production of automobiles in that year
B) An unsold inventory of automobiles produced in that year
C) An unused stock of goods produced in the previous year
D) The total amount of flour used by bakeries to make bread in that year
13) A factory in Techland could not sell 20 percent of its output during a certain year due to a decrease in the demand for its product. Which of the following would be true if it produced 20 percent less?
A) Techland's GDP for that year would have been higher.
B) Techland's GDP would have remained the same.
C) Techland's GDP for that year would have been lower.
D) Techland's income per capita for that year would have been higher.
14) There is only one firm in a small island country. The firm produced 1,000 units of Good X during a particular year, out of which it could sell 900 units. If each unit of the good sells for $500, what is the GDP of the country?
A) $40,000
B) $450,000
C) $500,000
D) $150,000
15) Which of the following is an example of physical capital?
A) A stock
B) A bond
C) A factory
D) A worker
16) If Dell buys a computer from a foreign producer for $500 and sells it to Best Buy for $800, who then sells it to a consumer for $1,200, what is Dell's value added, Best Buy's value added, and the computer's contribution to GDP?
A) $300, $400, and $1,200
B) $300, $700, and $1,000
C) $300, $400, and $700
D) $800, $1,200, and $400
17) Which of the following is considered a final good or service?
A) An airline ticket purchased to go on a business trip
B) The flour used by a baker to make bread
C) The bread purchased by a sub shop to make sandwiches
D) The steel used to make a car
18) Which of the following would not be included in the calculation of GDP?
A) The purchase of ice cream by a student at a store
B) The purchase of a new car by a family
C) The purchase of a steak by a customer at a restaurant
D) The purchase of a cow by a restaurant to turn into steaks
19) Which of the following is considered a final good or service?
A) An airline ticket purchased to go on a business trip
B) The flour used by a baker to make bread
C) The bread purchased by a sub shop to make sandwiches
D) The steel used to make a car
20) Workers in an economy are likely to be more productive if ________.
A) the size of the population is high
B) the economy has a large physical capital stock
C) the unemployment rate in the economy is low
D) the rate of inflation in the economy is high
21) Which of the following is an example of physical capital in agricultural production?
A) A road
B) A tractor
C) A farmer
D) A canal
22) The productivity of workers in an economy will be high if the economy has ________.
A) a large working age population
B) a negative rate of inflation
C) high levels of human capital
D) a small physical capital stock
23) The average years of schooling of workers in Argonia has increased. Which of the following is likely to be true if all other variables remain unchanged?
A) The efficiency units of labor in Argonia is likely to increase.
B) The income per worker in Argonia is likely to decrease.
C) The unemployment rate in Argonia is likely to increase.
D) The price level in Argonia is likely to decrease.
24) An economy with better technology is likely to ________.
A) use more labor than capital
B) achieve higher productivity
C) have a small physical capital stock
D) have lower levels of human capital
25) Suppose the average productivity of workers in Country A is equal to that of workers in Country B. If Country A has higher total efficiency units of labor than Country B, it implies that ________.
A) Country B has a larger supply of workers
B) Country A has a larger supply of workers
C) Country A has a larger stock of capital
D) Country B has a larger stock of capital
26) Assume Industry Country relies more heavily on the use of capital and Farm Country relies more heavily on the use of labor in production. Holding labor constant, which country's output would be more negatively affected by a big storm that destroys large parts of the existing infrastructure?
A) Industry Country
B) Labor Country
C) Both countries equally
D) Both countries equally if their initial GDP is equal
27) The total number of workers in two different countries is equal. However, workers in Country A are three times more productive than workers in Country B. Which of the following is true in this case?
A) The total efficiency units of labor in Country A is one-third the total efficiency units of labor in Country B.
B) The total efficiency units of labor in Country A is three times more than the total efficiency units of labor in Country B.
C) The physical capital stock in Country B is three times more than the physical capital stock in Country A.
D) The total efficiency units of labor in Country B is six times more than the total efficiency units of labor in Country B.
28) Which of the following is likely to increase the productivity of workers in an economy?
A) An increase in the price level
B) The discovery of an oil field
C) An increase in the labor force participation rate in the economy
D) An increase in the number of years of training that each worker receives
29) Which of the following is likely to lead to an increase in the GDP of a country?
A) An increase in the physical capital stock of the country
B) An increase in the unemployment rate in the country
C) An increase in the tax rates in the country
D) An increase in the interest rates in the country
Scenario: Two economies, A and B, have identical aggregate production functions with diminishing returns. In both economies, capital and labor are equally important for production. Economy A has twice as many efficiency units of labor as economy B. Economy B has twice as much physical capital stock as economy A.
30) Refer to the scenario above. If population doubles and GDP remains unchanged, the economies' ________.
A) GDP per capita will increase
B) average standard of living will decrease
C) income per capita will remain unchanged
D) productivity will increase
31) Refer to the scenario above. Economy A has a higher GDP if ________.
A) its working population is bigger than economy B's working population
7B) its population is better educated than economy B's population
C) its economy is not subject to the Law of Diminishing Marginal Product
D) it employs more advanced technology in production than does economy B
32) Inventia has 1 million workers. Suppose 50,000 workers migrate from a neighboring country to join Inventia's workforce. Which of the following will happen in this case if Inventia's physical capital stock remains unchanged?
A) The marginal contribution of labor to Inventia's output will fall.
B) The relationship between output and physical capital stock becomes negative.
C) The total efficiency units of labor in the economy will decrease.
D) The country's income per worker will increase.
33) The ________ in output due to each additional unit of a factor of production is ________ when other factors are held constant.
A) increase; smaller
B) increase; larger
C) decrease; smaller
D) decrease; larger
The following figure shows graphs of various types of growth.
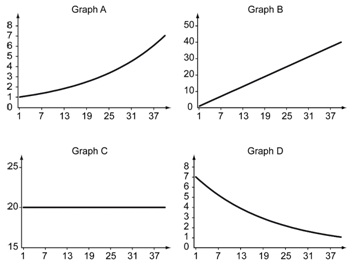
34) Refer to the figure above. The data in Graph A best represent ________.
A) linear growth
B) no growth
C) exponential growth
D) exponential decline
35) Refer to the figure above. The data in Graph B best represent ________.
A) linear growth
B) no growth
C) exponential growth
D) exponential decline
36) Refer to the figure above. The data in Graph C best represent ________.
A) linear growth
B) no growth
C) exponential growth
D) exponential decline
37) Refer to the figure above. The data in Graph D best represent ________.
A) linear growth
B) no growth
C) exponential growth
D) exponential decline
38) GDP per capita in Australia is $50,000. If Australian GDP per capita grows 6 percent per year for 2 years, which formula shows its GDP per capita after 2 years?
A) $50,000 × 1.06
B) $50,000 × 1.12
C) $50,000 × 1.06 × 1.06
D) $50,000 × 1.06 × 1.12
39) Initially Country A has a greater GDP per capita than Country B, but the growth rate in Country A is only 1 percent, while it is 2 percent in Country B. If these growth rates continue forever, which of the following is correct?
A) Country A will always have a higher GDP per capita than Country B.
B) Country B will not be able to sustain such a high growth rate.
C) The GDP per capita in Country B will eventually catch up to, but not overtake, that of Country A.
D) The GDP per capita in Country B will eventually overtake that of Country A.
Scenario: In 2000, world GDP per capita was $5,500. In 2010, world GDP per capita was $9,500.
40) Refer to the scenario above. If the world sustains this growth rate, approximately what will world GDP per capita be in 2020?
A) $13,500
B) $15,000
C) $16,400
D) $19,000
41) Refer to the scenario above. If the world sustains this growth rate, approximately what will world GDP per capita be in 2030?
A) $16,400
B) $17,500
C) $21,500
D) $28,300
42) The growth process whereby relatively poorer nations increase their income by taking advantage of knowledge and technologies already invented in other, technologically more advanced countries is known as ________ growth.
A) transfer
B) catch-up
C) trade-based
D) innovative
43) Catch-up growth is characterized by disparities in growth levels, magnified by the ________ nature of economic growth.
A) disproportionate
B) exponential
C) homogenous
D) linear
44) Sustained growth refers to a growth process in which ________.
A) GDP per capita grows at a positive and steady rate for long periods of time
B) GDP per capita grows at a rate of more than 20 percent per year for long periods of time
C) growth in GDP per capita is primarily attributed to public sector firms and enterprises
D) growth in GDP per capita is translated into an equal increase in welfare for all citizens in a country
45) U.S. GDP per capita has increased approximately 2 percent per year over an extended period. This is a good example of what sort of growth?
A) Catch-up growth
B) Power growth
C) Linear growth
D) Sustained growth
46) Assuming all else equal, if the production technology available to a nation improves, its ________.
A) GDP decreases
B) stock of physical capital decreases
C) GDP increases
D) population increases
47) The value of all equipment and structures in an economy is referred to as its ________.
A) national income
B) physical capital stock
C) wealth
D) asset value
The following table shows levels of consumption and investment in four countries.
|
Country A
|
Country B
|
Country C
|
Country D
|
|
Consumption
|
200
|
2,200
|
2,000
|
5,200
|
|
Investment
|
600
|
3,000
|
1,200
|
4,200
|
48) Refer to the table above. Which country has the highest savings rate?
A) Country A
B) Country B
C) Country C
D) Country D
49) Refer to the table above. Which country has the lowest consumption rate?
A) Country A
B) Country B
C) Country C
D) Country D
50) Which of the following statements is true of the U.S. economy before 1800?
A) There were no major achievements in arts in the U.S. economy.
B) There were no major achievements in science and technology in the U.S. economy.
C) Sustained economic growth was rare or absent in the U.S. economy.
D) The U.S. economy was growing at an average rate of more than 6 percent per year.