Assignment:
1. If you jump upward (on Earth) with an initial velocity of 3 m/s, how long will will it take before you return to the ground? How high will you have gone?
2. What is the gravitational potential energy of a 10 kg TV held 1 m off the ground? 10 m off the ground? 100 m off the ground?
3. You are moving a 100 kg refrigerator up a small staircase to a height of 1 m. You use a ramp that is 10 m long. What is the minimum amount of force along the ramp must you exert to push the refrigerator to the top?
4. A bolt requires 6 N m of torque to tighten. Using a wrench with a handle 10 cm long, how much force must you exert to turn the bolt?
5. On one side of a seesaw, a 10 kg child sits 2 m from the fulcrum (the balance point at the center of the seesaw). How far from the fulcrum must a 20 kg child sit on the other side to balance the seesaw?
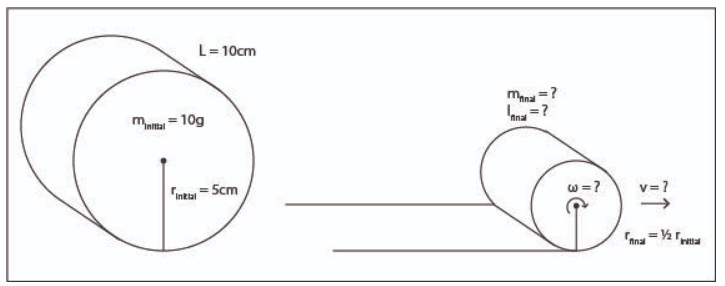
A roll of paper has initial mass minitial=10g, initial radius rinitial = 5cm and length L=10 cm.
(a) Calculate the density (density= mass/volume) of the roll of paper in units of kg/m3 kgm3. The volume V of a cylinder is V= π . r2 . L.
You give the paper a tiny push so it starts rolling forward. Assume that the push is so small that the initial kinetic energy is effectively zero.
(b) Calculate the gravitational potential energy of the roll of paper right at the moment it starts to move. Use the center of mass as the reference height.
It leaves behind a trail of paper, meaning that the mass decreases and the radius decreases as the paper rolls. We wish to determine how fast the paper is moving forward (velocity v) when it has rolled to where the radius is half the initial radius.
(c) Once the paper has rolled to where the radius is half the initial radius, what is the new mass? What is the "rotational mass" at this point? The "rotational mass" I of a cylinder may be calculated using I=1/2m . r2.
(d) Calculate the new gravitational potential energy. Write down an expression for the total kinetic energy (linear + rotational) of the paper in terms of the unknown linear velocity vV and the unknown angular velocity ω and your answers from part (c).
(e) Given that energy is conserved (total initial energy =total final energy) and that angular velocity is related to linear velocity by ω =v/rωvr, use your answers from parts (b) and (d) to calculate the forward velocity of the paper at the point where its radius is half the initial radius.