Assignment:
Introduction:
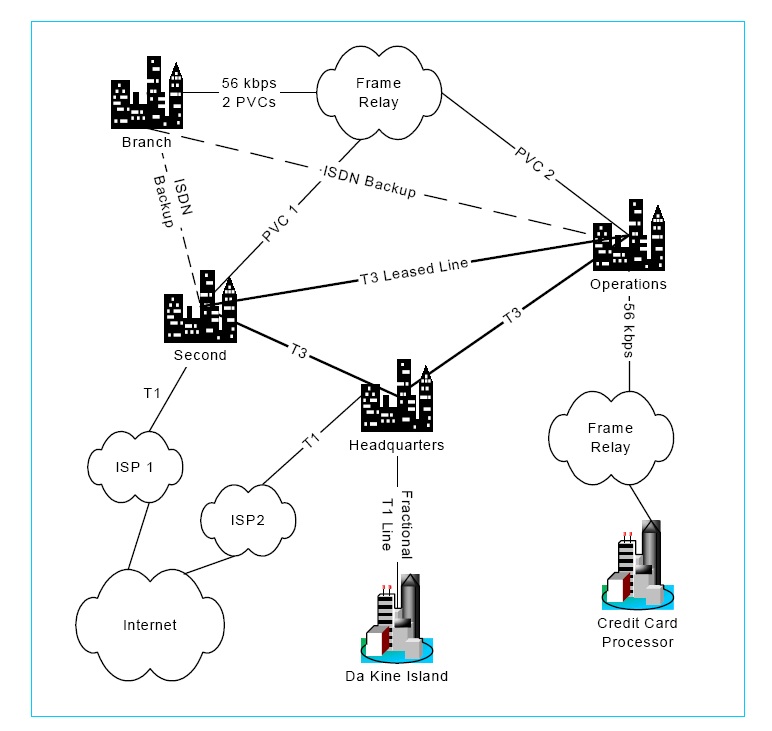
The First Bank of Paradise (FBP) operates primarily within the state of Hawaii, although it has one branch office on Da Kine Island in the South Pacific. FBP has 27 branch offices around the state. See the attached document for the bank's wide area network. (The diagram in the attachment does not exactly match the descriptive text in the problem specification. This is a notional diagram. Put more importance on the descriptive text and use the diagram "as is".)
Organizational Units:
Major Facilities:
The attached document shows that FBP has three major facilities, all located on
the island of Oahu.
- Headquarters is a downtown office building that houses the administrative staff.
- Operations is a building in an industrial area that houses the bank's mainframe operations and other back-office technical functions. It also has most of the bank's IT staff, including its networking staff.
- Second is a back-up facility. If Operations fails, Second can take over within minutes. Second is located in an otherwise agricultural area.
Branches:
Although branches are small buildings, they are complex technologically, primarily because the devices there use diverse network protocols. The automated teller machine at a branch uses SNA protocols to talk with the mainframe computer at Operations. The teller terminals use different SNA protocols to talk to the Operations mainframe. File servers require IPX/SPX communication, and branch offices that need Internet access require TCP/IP.
At each branch, there is a Cisco 2600 router to connect the branch to Operations. This is a multiprotocol router capable of handling the many protocols used at the internet and transport layers in branch office communication.
External Organizations:
First Bank of Paradise has to deal with several organizations outside the company. The attachment shows only one of these-a connection to a credit card processing center. In fact, the Bank deals with over a dozen outside support vendors, each in a different way. Fortunately, the credit card authorization firm uses TCP/IP, which simplifies matters.
The FBP Wide Area Network (WAN):
The attached document shows the complex group of WANs that the bank uses to hold together this geographically dispersed and technologically diverse collection of sites.
T3 Lines:
A mesh of T3 lines connects major facilities, as the attached document shows. T1 leased lines operate at 44.7 kbps, providing "fat pipes" between these facilities.
Branch Connections:
Branches are connected to the major facilities in two ways. Most of the time, they communicate via a Frame Relay network. For each branch, there are two 56 kbps PVCs. One leads to Operations, the other to Backup. They also have ISDN, as do the major facilities buildings.
Da Kine Island Branch:
For the Da Kine Island branch, the firm has a 128 kbps fractional T1 digital leased line.
Credit Card Service:
FBP connects to the credit card processing using a company 56 kbps Frame Relay network. This gives adequate speed.
Branch LANs:
Branch offices require complex internal networking because of their use of multiple protocols. Until recently, all networking in branch offices used 802.5 Token-Ring Networks, except for a few "rogue" devices, including automated teller machines, which required different connections. The bank is replacing its branch Token-Ring Networks with Ethernet networks on a staged basis over three years.
Internet Access:
For Internet access, FBP uses two separate ISPs, connecting to each via a T1 leased line. By limiting access to the Internet to two points, FBP enhances its security.
Problem:
- List all examples of redundancy in the FBP network.
- What is the goal of redundancy?
- Why are there only two access points to the Internet?
- Why do you think two access points were created instead of one?
- Do you think the bank uses the same Frame Relay network to connect its branches as it uses to connect to its credit card processing center?
- Why do you think the bank uses a fractional T1 line to its Da Kine Island branch
instead of a full T1 line? Instead of a Frame Relay connection?
- Why do you think the bank uses T3 lines to link its major facilities instead of using ATM?
Your answer must be typed, double-spaced, Times New Roman font (size 12), one-inch margins on all sides, APA format.