Assignment:
Question 1. If the active site of a dipeptidase contains a glutamic acid residue (pKa 3.3) and a histidine residue (pKa 6.7), both of which must be charged for the substrate to bind, what is the optimal pH for substrate binding?
Question 2. Lysozyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of C-O-C bonds between sugar residues in bacterial cell walls. The proposed catalytic mechanism for lysozyme requires that the side-chain group of aspartic acid-52 be in the ionized -COO- form and that of glutamic acid-35 be in the un-ionized -COOH form.
(a) What percentages of Asp and Glu side-chain groups would be in the ionized -COO- form at pH 5.0, the pH optimum for the hydrolysis of chitin by lysozyme, assuming pKas for the side-chains as given in Table of Garrett and Grisham?
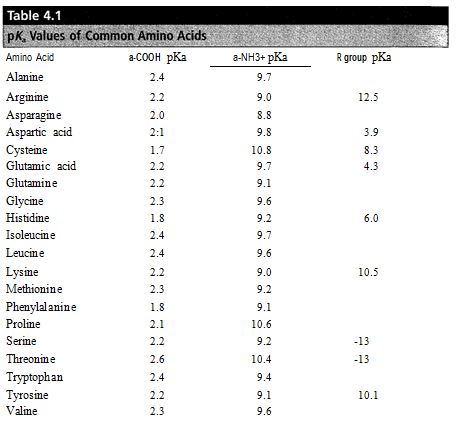
(b) In view of your answer to part (a), explain how it is possible for Glu-35 in lysozyme to be present in the un-ionized form.
Question 3. A solution which contains a mixture of three tripeptides -- 1) Tyr-Arg-Ser, 2) Glu-Cys-Phe, and 3) Asp-Asp-His -- is chromatographed on CM-cellulose at three different pHs: 6.0 8.0, and 10.0. In what order will each of the peptides emerge from the column at each of these pHs? Use Table 4.1 in the Garrett and Grisham text for amino acid pKas. The pKa for the CM-cellulose is 4.90.
Provide complete and step by step solution for the question and show calculations and use formulas.