Use the given chart to answer questions from 1-3:
Assume that labor can produce flowers or candy in the US and Sweden. Below is the chart that points out how much 1 hour of labor can produce if it specializes in a particular good.
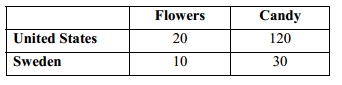
Question 1: Which of the given is true?
a. US have an absolute benefit in flowers.
b. Sweden has a comparative benefit in flowers.
c. Sweden has a comparative benefit in candy.
d. Both (a) and (b).
e. None of the above.
Question 2: Both countries would benefit if:
a. US produced both commodities and didn’t trade with Sweden.
b. Sweden generated both commodities and didn’t trade with the US.
c. United States exported candy and imported flowers.
d. United States exported flowers and imported candy.
e. None of above.
Question 3: There would be no international exchange rate which would permit mutually advantageous exchange between the US and Sweden if the output/labor for candy in Sweden was, rather than 30:
a. 5
b. 10
c. 60
d. 120
e. 200
Question 4: Assume that there are two factors, land and capital, and that the US is relatively capital abundant while Mexico is relatively land abundant. According to the H-O theory,
a. Mexican landowners must support Mexican-US free trade.
b. Mexican capitalists must oppose Mexican-US free trade.
c. US capitalists must support Mexican-US free trade.
d. All of the above.
Question 5: If Canada imposes a tariff on bananas and if none are grown in Canada, this tariff has:
a. Only revenue effects.
b. Only protective effects.
c. Both protective and revenue effects.
d. Neither revenue nor protective effects.