Aim: This assignment is designed to help you improve your critical thinking and problem solving skills, as well as your information literacy skills (i.e. the ability to select and organise information and to communicate it effectively and ethically).
Problem 1: Using CRC-8 with generator g(x) = x8 + x2 + x + 1, and the information sequence 1000100101.
(a) Find the (18, 10) codeword (i.e., codeword is 18 bits, where the message is 10 bits) corresponding to the preceding information sequence.
(b) Suppose that the codeword is transmitted with no error. Demonstrate how the receiver extracts the message from codeword?
(c) Prove that this generator enables to detect single bit errors.
(c) Assuming that the system detects 2-bit errors, and let the receiver knows there is a single bit error in the transmission. Can the receiver detects the error bit, and thus, obtain the correct message? Defend your answer.
Problem 2: Figure 1 shows three sine waves. For each wave answer the following questions:
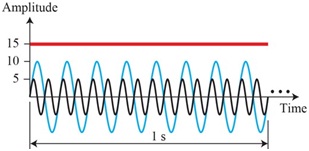
Figure 1: Time domain presentation of three sine waves
(i) What is the frequency, period, amplitude, and phase of the wave shown in black color?
(ii) What is the frequency, period, amplitude, and phase of the wave shown in blue color?
(iii) What is the frequency, period, amplitude, and phase of the wave shown in red color?
Problem 3: For dataword 1001 (which is represented as x3 + 1) and the divisor 1011 (which is represented as x3 + x + 1), the sender calculates a (7, 3) CRC codeword 1001110 and sends it to the receiver.
(i) Because of the noise in transmission medium, however, the receiver receives 1100010. Discuss whether or not the receiver accepts the codeword? If yes, is the accepted data correct?
(ii) Is it possible that the codeword be modified, but the receiver obtains a correct data? If yes, give your argument and provide such a modified codeword.
Question 4: An organization is granted a block of addresses with the beginning address 140.42.74.0/24. the organization needs to have 3 blocks of addresses to use in its three subnets: one subnet of 12 addresses, one subblock of 55 addresses, and one subblock of 125 addresses.
(i) Design the subblocks. Determine the first address and last address in each block, using binary, dotted decimal, and Hexadecimal notation.
(ii) How many addresses are left in reserve?
Problem 5: An IP datagram has arrived with the following information in the header (in hexadecimal) - see Figure 2:
4500 001C C001 0000 0411 0000 0A0C 0E05 0C06 0709

Figure 2: An IP datagram header format
(i) What is the header size?
(ii) Are there any options in the packet?
(iii) What is the size of the data?
(iv) Is the packet fragmented?
(v) How many more routers can the packet travel to?
(vi) What is the protocol number of the payload being carried by the packet?
Problem 6: For the above question, calculate the header checksum.
Problem 7: Figure 3 shows a scenario of Stop-and-Wait protocol.
Give a detail explanation of this Figure. That is, begin from sender's clock, window value, and the packet number. Then describe actions taken by the receiver, i.e., changing the window's value and sending ACK (by justifying the ACK number). Continue the explanation for all rows/transmissions in the Figure.
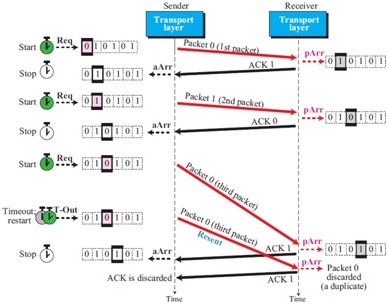
Figure 3: A scenario of Stop-and-Wait protocol
Problem 8: In a network using the Go-Back-N protocol with m = 3 and the sending window of size 7, the values are Sf = 42, Sn = 46, and Rn = 44. Assume that the network does not duplicate or reorder the packets.
(i) What are the sequence numbers of data packets is transit?
(ii) what are the acknowledgment numbers of data packets in transit?
Problem 9: The following is part of a TCP header dump (contents) in binary format (see Figure 4): 1110 0010 1000 0101 0000 0000 0001 1000
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
1000 0000 0000 0010 0000 0111 1111 1111
...
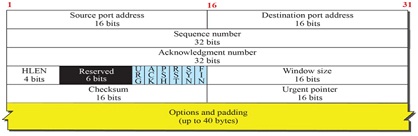
Figure 4: TCP header format
(i) What is the source port number (in decimal format)?
(ii) What is the destination port number (in decimal format)?
(iii) What is the length of the header?
(iv) Is there any option? If yes, what is the size of option?
(v) What is the type of the segment?
(vi) What is the window size?
With the professional assistance of Advanced Data Communications Principles Assignment Help service, you will always be able to fetch top grades without putting your hands into the tedious job of assignment writing.
Tags: Advanced Data Communications Principles Assignment Help, Advanced Data Communications Principles Homework Help, Advanced Data Communications Principles Coursework, Advanced Data Communications Principles Solved Assignments, Stop-and-Wait Protocol Assignment Help, Stop-and-Wait Protocol Homework Help, Go-Back-N Protocol Assignment Help, Go-Back-N Protocol Homework Help
Attachment:- Advanced Data Communications Principles.rar