I. Suppose an influenza epidemic strikes a city. In 10% of families the mother has influenza; in 10% of families the father has influenza; and in 2% of families both the mother and father have influenza.
a. Are the events A1 = {mother has influence} and A2 = {father has influenza} independent?
II. The following table gives a two-way classification, based on gender and employment status, of the civilian labor force age 16 to 24 years as of July 2002. The numbers in the table are in thousands.
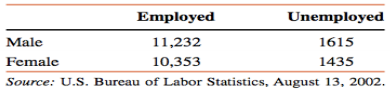
a. If one person is selected at random from these young persons, find the probability that this person is
i. unemployed
ii. a female
iii. employed given the person is male
iv. a female given the person is unemployed
b. Are the events "employed" and "unemployed" mutually exclusive? What about the events "unemployed" and "male"?
c. Are the events "female" and "employed" independent? Why or why not?
III. A random sample of 250 juniors majoring in psychology or communications at a large university is selected. The students are asked whether or not they are happy with their majors. The following table gives the results of the survey. Assume that none of these 250 students is majoring in two areas

a. If one student is selected at random from this group, find the probability that this student is
i. happy with the choice of major
ii. a psychology major
iii. a communications major given that the student is happy with the choice of major
iv. unhappy with the choice of major given that the student is a psychology major
v. a psychology major and is happy with that major
vi. a communications major or is unhappy with his or her major
b. Are the events "psychology major" and "happy with major" independent? Are they mutually exclusive? Explain why or why not.
IV. A group of 2000 randomly selected adults were asked if they are in favor of or against cloning. The following table gives the responses.
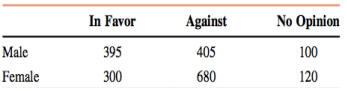
a. If one person is selected at random from these 2000 adults, find the probability that this person is
i. in favor of cloning
ii. against cloning
iii. in favor of cloning given the person is a female
iv. a male given the person has no opinion
b. Are the events "male" and "in favor" mutually exclusive? What about the events "in favor" and "against"? Why or why not?
c. Are the events "female" and "no opinion" independent? Why or why not?
V. Two fair dice, one red and one green, are rolled. Let the event A be "the sum of the faces showing is equal to seven." Let the event B be "the faces showing on the two dice are equal'.
(a) List out the sample space of the experiment.
(b) List the outcomes in A, and find P(A).
(c) List the outcomes in B, and find P(B).
(d) List the outcomes in A ∩ B, and find P(A ∩B)
(e) Are the events A and B independent? Explain why or why not.
(f) How would you describe the relationship between event A and event B.