Assignment:
Question 1: Quick check/short answer
Use the following wage-setting and price-setting equations to briefly answer the following questions. Refer to the textbook and class notes for variable definitions.
W = Pe F(u, z)
P = (1+ m)W /A
a. Wage setting:
i. List three examples of labor market institutions included in the parameter z.
ii. Explain how an increase in the unemployment rate will affect nominal wages.
b. Price setting: Why can firms set prices set above unit labor costs?
Question 2: Recent labor market trends and evidence for the U.S. economy
Read the article posted on Blackboard with this assignment about the February jobs report for the U.S. economy. (But also note that the March jobs report will be released this Friday a.m.!).
a. What are two useful pieces of information from the article for understanding what's going on in the U.S. labor market?
b. What are two pieces of information that are not discussed in the article, that you would like to know in order to evaluate how well the U.S. labor market is doing? (Use your class notes and Sections 7-1 & 7-2 in the book to help you brainstorm).
Question 3: The natural rate of unemployment
Suppose that the mark-up of goods prices over unit costs is 5%, and the wage-setting equation is W = Pe(1 - u) where u is the unemployment rate. Set labor productivity (A) to 1.
a. What is the price-setting equation for this economy (i.e. when the mark-up is 5%)?
b. Use your answer to (a) to solve for the real wage.
c. What is the natural rate of unemployment? (Remember, the natural rate of unemployment is the unemployment rate when wage- and price-setting are both satisfied).
d. Suppose the mark-up increases to 10%. What happens to the natural rate of unemployment? Support your answer with the graphical description of the labor market.
Question 4: Use the labor market model to analyze the effects of the following shocks on real wages and unemployment. In each case, show your answer graphically, and explain what variable in wage- or price-setting is affected by the shock (z, in, u, etc.).
a. The Federal Trade Commission allows Amazon to acquire Whole Foods.
b. There is the following long-term trend in unionization rates in the U.S. economy (see Figure on pg. 2).
Figure: Unionization rates in the U.S. economy (1983 to 2017)
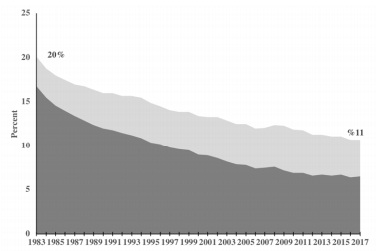
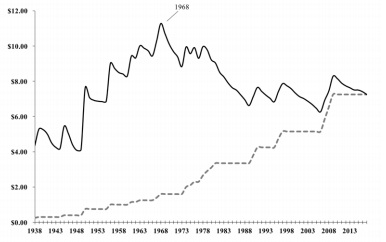
c. There are the following trends in the real and nominal federal minimum wage in the U.S. economy. [Hint: why should your answer refer to the real minimum wage?].
Figure: The federal minimum wage in the U.S. economy (1938 to 2017)
Readings:
The Jobs Report Was the Weakest in Months. Here's Why.
By Patricia Cohen