Question: Enzyme kinetics
For an enzyme that follows Michealis-Menten kinetics, the initial velocity at different substrate concentration has been determined.

a) Determine KM and VMAX.
b) The experiments are replicated with addition of a reversible inhibitor (the new results are shown in below table). Determine the effect of the inhibitor on KM and VMAX and the type of inhibition.

c) Calculate the enzyme concentration in the reaction mix, when the turnover number of the enzyme, kcat is 250 s-1.
Question: Batch fermentation
For aerobic cultivation of yeast the cell mass concentration, Xt, and the concentration of the limiting substrate component (glucose), St, has been determined.
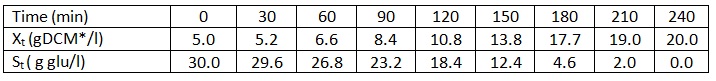
a) Calculate the average cell mass yield factor, YX/S in this fermentation.
b) Calculate the maximum specific growth rate, μMAX, in the logarithmic growth phase.
c) Calculate the volumetric growth rate, dX/dt = rX at time=125 min.
d) Calculate the volumetric substrate utilization rate, rS, and the specific substrate utilization rate, qS, of the yeast at time = 170 min, assuming that the average yield factor can be used to determine rS.
e) Calculate the concentration of left over substrate at time = 130, again assuming that the average yield factor can be used.
Question: Continuous (chemostat) fermentation
A genetically modified yeast is cultivated at pH = 3.3 and temperature = 37oC). Values of substrate flow, F, cell mass concentration, X1, concentration of glucose, S1 (the limiting substrate component), and product concentration, P1, was measures throughout fermentation. The product is a protein – not a primary metabolite – and the substrate utilization for product formation, rS = YX/P,stoich . qp . X, is so low that it can be neglected. All samples were taken after steady state had been established. The feed stream, S0, contains 50.0 g glu/l and no product (P0 = 0), and the working volume, V, is 500 ml. ke = kd = 0.
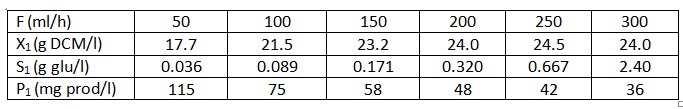
a) Explain ke and kd.
b) Examine if the growth if following Monod kinetics and if this is the case determine KS and μMAX.
c) Examine if the substrate utilization kinetics can be expressed by growth constants YX/S, true and mS and if this is the case calculate these constants.
d) At D = 0.46 h-1 and same conditions as given above calculate YX/S, rX, rS, rP, and YP/S.