Assignment:
Instructions: Unless otherwise indicated, please make all answers to 2 decimal places
QUESTION 1 The two general approaches to forecasting are:
A. Delphi and Exponential Smoothing
B. Time Series and Regression
C. Qualitative and Time Series
D. Qualitative and Quantitative
QUESTION 2 Which of the following features would generally be considered to be common to all forecasts:
A. Actual results will differ somewhat from predicted values
B. Assumption of a stable underlying causal system
C. Forecasts for groups of items tend to be more accurate than forecasts for individual items
D. Historical data is available on which to base the forecast
E. Accuracy decreases as the time horizon increases
QUESTION 3 The elimination of [a] is one of the major goals of lean manufacturing.
QUESTION 4 Which of the following is a way to measure forecast accuracy (check all that apply):
A. MAPE
B. MRP
C. MSE
D. WMAPE
QUESTION 5 Which of the following is not an assumption of the EOQ model?
A. Lead times do not vary
B. Forecasts are known, constant and accurate
C. Each order is received in a single delivery
D. Quantity discounts are available
E. All of these are assumptions in the EOQ model
QUESTION 6 The purpose of cycle counting is:
A. reduce theft
B. avoid having to do an annual physical inventory
C. reduce discrepancies between the inventory records and actual inventories
D. count 10% of the items each month
E. to count all the items in inventory
QUESTION 7 A risk avoider would want [a] safety stock.
QUESTION 8 Systems use visual signals to control the amount of inventory in the system.
QUESTION 9 If there are no variations in either lead time or demand, the re-order point (ROP) will equal:
A. expected usage during the lead time
B. safety stock
C. the EOQ
D. the service level
E. EOQ plus safety stock
QUESTION 10 Which of the following does not impact the amount of inventory carried Q
A. type of inventory management practiced (periodic vs. perpetual)
B. lead time
C. number of warehouses stocking the same item
D. number of items in the catalog
QUESTION 11 A refers to a phenomenon where small variations in customer demand are magnified through the supply chain, resulting in large variations at the factory.
QUESTION 12 A demand pattern characterized by a spike in sales at the end of the quarter and a decline in sales at the beginning of the quarter is called [b]
QUESTION 13 In systems, work is scheduled on the basis of the forecast net of the inventory rather than waiting for a down stream signal that product is needed.
QUESTION 14 A method where trading partners agree that the supplier will manage the inventories at the customer in exchange for committing to service level and inventory turn over objectives is called:
A. JIT2
B. Vendor Owned Inventory
C. VMI
D. CPFR
QUESTION 15 Demand management includes all of the following except:
A. Planning demand
B. Communicating demand
C. Manipulating demand
D. Influincing demand
E. All of these (Planning, Communicating, Manipulating and Influincing) are elements of Demand Management.
QUESTION 16 Is a pricing policy that works to eliminate variations in demand caused by sales and promotions.
QUESTION 17 MRP schedules items that have either exclusively or primarily [a] demand.
QUESTION 18 Contains a listing of all the assemblies, parts and materials needed to produce one unit of an end item.
QUESTION 19 Which of the following is NOT an example of muda?
A. Extraneous processing steps
B. Movement of people to the work
C. Defects
D. Downstream workers training on SPC
E. Inventory
F. Movement of goods
G. Goods or services that to not meet customer needs
QUESTION 20 Shows the capacity requirements vs. capacity for departments or work centers.
QUESTION 21 MRP does not guarantee a feasible production plan
True
False
QUESTION 22 Part A is produced in fixed lots of 110 each. The net requirements in week 48 are 203 units. How many lots does MRP scheduled to produce in week 48?
QUESTION 23 A service garage uses 120 boxes of cleaning cloths per year. The boxes cost $6/each. It costs the garage $3 to place an order and the holding costs are 10% of the purchase price unit per year. Determine the EOQ for this item (2 decimal places).
QUESTION 24 A service garage uses 120 boxes of cleaning cloths per year. The boxes cost $6/each. Ordering costs are $3/order. Holding cost is 10% of the purchase price per unit per year. What is the total cost (TC) to the garage for purchsing this item annually (2 decimal places)? Use EOQ rounded to the nearest whole number.
QUESTION 25 A service garage uses 120 boxes of cleaning cloths per year. The boxes cost $6/each. Ordering costs are $3/order and holding cost is 10% of the purchase price per box per year. The supplier is offering a purchase price break. If the garage orders 50 boxes per order, the price will be reduced to $5.75 per box. What is the total cost (TC) at Q=50?
QUESTION 26 Which of the following is not a location option that management could consider in location planning?
A. expand an existing facility
B. add a new location/facility
C. move from one location to another
D. do nothing
E. all of these are options management may consider
QUESTION 27 In location planning, the location of raw materials, location of markets and labor factors are:
A. regional factors
B. community factors
C. site-related factors
D. national factors
F. minor considerations
QUESTION 28 A company is looking to build a new factory. Hartford, CT and Akron, OH are two possible locations and local governments have made pitches to the company for their city. The company has decided to weight three factors in making the decision:
A. 50% - location of raw materials
B. 10% labor costs
C. 40% transportation costs.
They have a scoring scale from 0-100 for each factor. They further decided that the winning location must have a score of at least 75. Hartford scores 70 for raw materials, 50 for transportation and 90 for labor. Akron scores 60 for raw materials, 80 for transportation and 70 for labor.
Should the company chose Hartford, Akron or neither? [a]
QUESTION 29 A small company makes hydraulic systems. The demand for one of their models for the last six months has been: 48, 53, 64, 57, 61 and 59 units. If the company uses a six month moving average technique, what would the next month's forecast be? Do not round the answer.
QUESTION 30 A small company makes hydraulic systems. The demand for one of their models for the last six months has been: 48, 53, 64, 57, 61 and 59 units. If the company uses a three month moving average technique, what would the next month's forecast be? Do not round the answer.
QUESTION 31 A small company makes hydraulic systems. The demand for one of their models for the last six months has been: 48, 53, 64, 57, 61 and 59 units. The forecast for last month was 64 units. If the company uses an exponential smoothing technique with alpha = .15, what would the next month's forecast be? Do not round the answer.
QUESTION 32 A small company makes hydraulic systems. The demand for one of their models for the last six months has been: 48, 53, 64, 57, 61 and 59 units. The forecast for last month was 64 units. If the company uses an exponential smoothing technique with alpha = .10, what would the next month's forecast be? Do not round the answer.
QUESTION 33 Is the strategy where a company makes each product in only one plant.
QUESTION 34 When making an outsourcing decision, companies should take into account all of hte following except:
A. Ownership of intellectual property
B. Potential creation fo a competitor
C. Loss of control over quality
D. Fair labor practices
E. Demographics
QUESTION 35 Using information from the table below, calculate MAPE:
|
Part
|
Forecast
|
Actual
|
|
ABC
|
12
|
18
|
|
DEF
|
32
|
26
|
|
GHI
|
953
|
881
|
|
JKL
|
4
|
13
|
|
MNO
|
6694
|
7058
|
When entering the answer, remember that the P in MAPE is percent. Do not enter the answer in decimal format. For example, .1234 would be incorrect format while 12.34 would be in the right format. Do not round your answer.
QUESTION 36 A bakery's use of corn sweetener is normally distributed with a mean of 80 gallons per day and a standard deviation of 4 gallons per day. Lead time for delivery of the corn sweetener is normally distributed with a mean of 6 days and a standard deviation of 2 days. If the manager wants a 99% service rate, what should the reorder point be (ROP). Round to the nearest whole number.
QUESTION 37 A bakery's use of corn syrup is normally distributed with a mean of 80 gallons per day and a standard deviation of 4 gallons. The lead time is normally distributed with a mean of 6 days and a standard deviation of two days. If the manager wants a 95% service rate, what sefety stock should she set (round to the nearest whole number)?
QUESTION 38 Ideas for new designs may come from (mark all that apply):
A. Customers
B. Employees
C. Competitors
D. R&D
QUESTION 39 A manufacturing company forecasts to sell 220 units in the month of November. As of October 25th, they have orders for 60 units the week of 11/2, 40 units the week of 11/9 and 17 units the week of 11/16. Safety stock is 5 units and the starting inventory is 70 units. What is the projected on hand in the week of 11/2?
QUESTION 40 A House of Quality is achieved when no department at a single location has more than 2% reject rates.
True
False
QUESTION 41. Match the manufacturing process type with the correct description
- Best for customized goods and services
- Used for semi-standardized goods and services
- Best for standardized goods and services, especially in higher volumes
- Highly standardized goods and services. Often more associated with processing than assembly.
A. Job Shop
B. Continuous
C. Repetitive
D. Batch
QUESTION 42 Service design differs from product design in that:
A. There is no difference
B. There is a lesser requirement to be aware of competitors' offerings
C. There is less visibility to customers
D. There is less latitude for finding and correcting errors prior to delivery
E. Service design tends to focus on tengible factors
QUESTION 43 In Lean Manufacturing, waste and inefficiency are referred to as __________ and the ongoing focused efforts to reduce this are called ____________ events.
QUESTION 44 ?If 17 P's are needed and no inventory is on hand for any component, what is the net requirement for Cs?
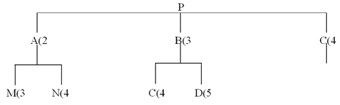
QUESTION 45
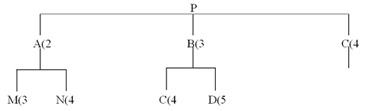
If part M is produced in fixed lots of 40/each and net requirements for M are 51 in week 6, what quantity will MRP schedule for Planned Receipts in week 6?
QUESTION 46 A manufacturing company forecasts to sell 440 units in May. They have orders for 95 units in week 1, 80 units in week 2 and 40 units in week 3. Safety stock is 50 units. The product is made in fixed lots of 200 units. They begin May with 140 units in stock. What quantity does MPS schedule for week 3?
QUESTION 47
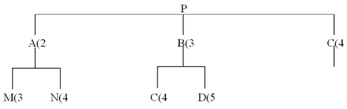
MPS schedules 40 P's for week 9. Projected on hand for week 9 are 15 A's. What are the net requirements for A's in week 9?
QUESTION 48 The core of Theory of Constraints consists of which three components:
A. Implement Drum Buffer Rope (DBR)
Manage the buffers
Use throughput accounting to guide decisions
B. Value Stream Mapping
Flow
Pull
C. Implement Drum Buffer Rope (DBR)
Flow
Manage the buffers
D. Value Stream Analysis
Implement Drum Buffer Rope (DBR)
Use throughput accounting to manage the buffers
QUESTION 49 A manufacturing company has implemented the Theory of Constraints to manage their production. At their Cheshire, CT plant, they have a constrained production line that can make three different products. They use throughput accounting to guide their decisions. For each product, what is the throughput per each using this information:
Product Price Cost Throughput
Alpha $22.50 $10.25
Delta $40.00 $32.5
Zulu $25.00 $15.00
QUESTION 50 A manufacturing company has implemented the Theory of Constraints to manage their production. At their Cheshire, CT plant, they have a constrainedproduction line that can make three different products. They use throughput accounting to guide their decisions. For each product, what is the throughput per each using this information:
Product Price Cost Time on constrained operation to make 1 EA
Alpha $22.50 $10.25 5 mins
Delta $40.00 $32.5 10 mins
Zulu $25.00 $15.00 15 mins
If the scheduler has one hour of time available on the constraint and all the materials are on hand to make any of the products, which one should she schedule?