Assignment question:
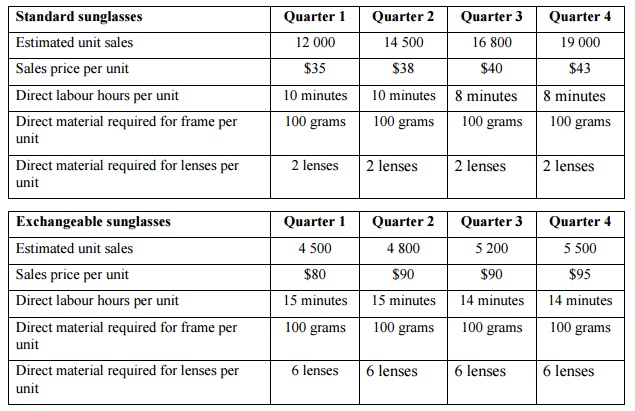
Xepa Ltd makes and sells two types (Standard and Exchangeable) of sunglasses. For the fourth quarter of 2015, the company sold 15 000 Standard sunglasses at $35 each and 5000 Exchangeable sunglasses at $60 each. The following data are available for the 2016 calendar year budget:
Both products use the same direct materials and are manufactured by the same labourers. Direct materials for the frames are bought in kilograms. Following are the costs for Direct Materials and the rates for Direct Labour for the relevant periods:
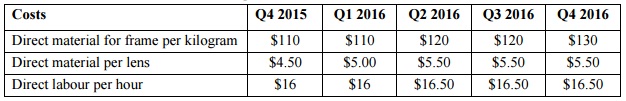
The direct labour rate includes wages, all employee-related benefits, and the employer’s share of payroll tax. The company’s enterprise agreement calls for an increase in direct labour wages on 1 April every year (the first day of the second quarter). The increase from 1 April 2015 has been included in the direct labour hourly rate above. The current machinery has been in operation since 2013 and the direct labour hours and the quantity of the direct materials required per unit of quarter 1 2016 has been the standard since then. New and improved machinery will be fully operational on 1 July 2016, hence the reduction in the direct labour time required per unit.
Management desires an ending inventory of finished goods units each quarter equal to 50 per cent of the next quarter’s sales units. Management also desires an ending inventory of all raw materials (both frames and lenses) equal to 75% of the particular quarter’s quantities used. The raw material inventory on 31 December 2015 was as follows: 1 369 kilograms of material for frames and 41 625 lenses.
The manufacturing overhead costs change twice a year: on the 1st of April and on the 1st of October. The variable cost per Direct Manufacturing Labour Hour (DMLH) rate is the same for both products. The following table summarises the manufacturing overhead costs relevant to the period of the budget, effective from the following dates:
1/10/2015 1/4/2016 1/10/2016
Variable cost per DMLH $4.00 $4.20 $4.40
Total fixed costs for six months (allocated equally p.m.) $33 000 $34 800 $36 000
The company calculates the fixed costs per unit for each quarter based on the total number of sunglasses produced in the relevant quarter.
Assume the following in your answer:
- Direct materials inventory and finished goods inventory are costed using the FIFO method.
- There is no work-in-progress inventory at any given point in time.
REQUIRED:
A) Design one input and the seven output sheets as required below. Ensure your spreadsheets meet the “design of spreadsheets” and “formatting” requirements as stated above.
Show the calculations for the two products separately (as illustrated in Example Ltd on p.3 of this assignment) for budgets 1, 2, 3, 4 and 6 below. Also show the calculations of the two products separately unless informed otherwise.
B) Prepare the following five (5) budgets for the first and second quarter of 2016 and the totals for the first half of the year. Also show at the bottom of each of these 5 budgets the total dollar value that will be shown in the Income Statement (required in budget 7).
1. Revenue
2. Production budget in units. Include a column to the left of the Q1 2016 column and show the figures for Q4 of 2015.
3. Direct material usage in quantity and dollars. First calculate the quantities, splitting the quantity of frames from the quantity of lenses. Show the quantity used for Q4 2015 in a column on the left hand side of the Q1 2016 column. Separate the direct materials used for the frames from the direct materials used for the lenses. Show the kilograms of DM for the frames used and the number of lenses per product per quarter and for the half year. Then add the total kilograms of DM used for lenses for both products per quarter and for the half year together (and do the same for the number of lenses) and show these figures. (Tip: You require the total figures of kilograms of material for frames and the number of lenses for the period ending 30 June 2016 to calculate the quantities and dollar values of direct material to be purchased for the half year. There is no need to calculate the cost used and/or purchased per product or per quarter, you only have to calculate these figures for the period ending 30 June 2016). (Refer to Schedule 3A on page 383 of the prescribed textbook for guidance as to how to calculate the quantity and dollar amounts of the direct materials that need to be purchased for the 6 months ending 30 June 2016).
4. Direct manufacturing labour costs. Calculate first the DMLH per product separately and then add the DMLH of the two products together. Then calculate the DML costs for the relevant periods.
5. Manufacturing overhead costs. Show the total DMLH of both products (calculated and shown in budget 4 above) per quarter and use these figures to calculate the variable costs for the required periods. (Please do not show the overhead costs for the two products separately).
Prepare the following two (2) budgets for the first half of 2016. Do not prepare it per quarter.
6. Finished Goods inventory: beginning and ending (Show the calculations of the cost per unit for the beginning and for the closing inventory for each product). Please do not show the Raw Materials inventory.
7. Income Statement. Use the absorption costing method and show the following line items: cost of goods manufactured, cost of goods available for sale, and cost of goods sold. Add a column to show which budget these figures are linked with. Do not show any cents in your figures in this budget.