Assignment:
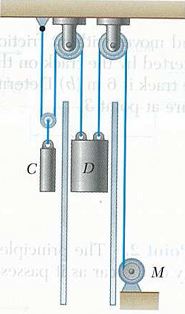
Question 1.The dumbwaiter D and its load have a combined mass of 300kg, while the counterweight C has a mass of 400 kg. Determine the power delivered by the electric motor M when the dumbwaiter:
(a) is moving up at a constant speed of 2.5 m/s;
(b) has an instantaneous velocity of 2.5 m/s and an acceleration of 0.75 m/s^2, both directed upward.
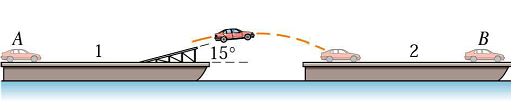
Question 2. Two barges, each with a displacement (mass) of 500 Mg, are loosely moored in calm water. A stunt driver starts his 1500 kg car from rest at A, drives along the deck, and leaves the end of the 15°ramp at a speed of 50 km/h relative to the barge and ramp. The driver successfully jumps the gap and brings his car to rest relative to barge 2 at B.
Calculate the velocity v2 imparted to barge 2 just after the car has come to rest on the barge. Neglect the resistance of the water to motion at the low velocities involved.
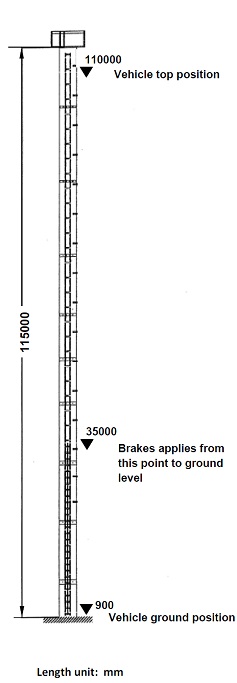
Question 3. The figure shows the drop tower in Dream World at Gold Coast. The major dimensions are shown in the figure. The carriage mass is 1523 kg and carries a maximum number of 8 riders with an average of 75 kg per person. The vehicle drops from the rest position at a height of 110000mm until the position at 35000mm from the ground level. After this position, constant brakes are applied to slow the vehicle down. Assuming there is no friction force along the track:
1) Calculate the velocity at the position where the brakes start to engage;
2) Calculate the deceleration during braking; and
3) Using the energy method, calculate the brake force and the energy required to bring the carriage to a stop (900mm above ground level).