Solve the following problem:
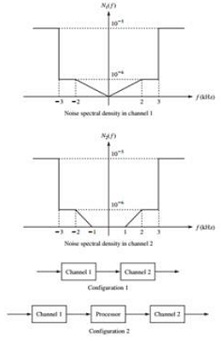
Channels 1 and 2 are both continuous-time additive Gaussian noise channels described by Y1(t) = X1(t) + Z1(t) and Y2(t) = X2(t) + Z2(t), respectively. Z1(t) and Z2(t) are the noise processes of the channels. It is assumed that Z1(t) and Z2(t) are zero-mean, independent Gaussian processes with power spectral densities N1( f ) and N2( f ) W/Hz, as shown in Figure. It is assumed that each channel has an input power constraint of 10 mW.
1. Determine C1 and C2, the capacities of the two channels (in bits per second).
2. If a binary memory less source with P(U = 0) = 1-P(U = 1) = 0.4 which generates 7500 symbols per second is to be transmitted once via channel 1 and once via channel 2, determine in each case the absolute minimum achievable error probability.
3. Now consider the two channel configurations shown in Figure . The first configuration is simply a concatenation of the two original channels. The second concatenation allows a processor with arbitrary complexity to be used between the two channels. In each case determine the absolute minimum achievable error probability for the binary source of part 2 when transmitted over the given channel configuration.
4. What is the capacity of channel 1 if the input power constraint is increased from 10 to 100 mW?